
Ancient civilizations have significantly shaped modern society through various advancements in culture, technology, governance, and other fields. By understanding and appreciating these contributions, we gain insight into the development and progression of human civilization. This report explores how several ancient civilizations have influenced today's world.
Technological and Agricultural Advancements
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia, often recognized as the world's first civilization, made numerous contributions that are still relevant today. One of the most notable is the invention of cuneiform writing, which revolutionized communication and record-keeping[3]. Mesopotamians also developed one of the earliest known calendars, structured around lunar phases and effectively used agriculture, influencing modern calendar systems[3]. The plow, another Mesopotamian invention, significantly enhanced agricultural productivity and remains foundational in modern farming[3]. Additionally, Mesopotamians invented the wheel and established the first forms of urban planning and irrigation systems[1][3][5].
Egypt
The ancient Egyptians were pioneers in various fields, particularly in architecture and engineering. Their pyramids and temples exemplify advanced building techniques and a deep knowledge of mathematics[2]. Egyptians also made significant medical advancements, including the development of surgical methods and the use of herbs and drugs, which influence medical practices even today[1][5][7]. They contributed to the field of writing through the creation of hieroglyphics, one of the earliest writing systems, influencing modern alphabets and written communication[2][3][5].
China
Ancient China was a powerhouse of innovation. Chinese inventions such as paper, printing, gunpowder, and the compass are integral parts of modern technology[1][2][3]. The Chinese also made early advancements in silk production, block printing, and acupuncture, which remain relevant in today's textile industry, publishing, and healthcare[1][5][6].
Philosophical and Scientific Contributions
Greece
Ancient Greece is renowned for its contributions to philosophy, democracy, and science. Philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle laid the foundational principles of Western philosophy, which shaped modern critical thinking, ethics, and political theory[2][10]. The concept of democracy, pioneered in Athens, forms the basis of many contemporary political systems[4]. Furthermore, Greek advancements in science and mathematics, including the work of Pythagoras and Hippocrates, continue to underpin modern scientific and mathematical thought[1][10].
India
India's ancient civilization contributed profoundly to philosophical thought, mathematics, and medicine. The concept of zero and the decimal system, developed by Indian mathematicians, revolutionized mathematics globally[2][3]. Moreover, Indian philosophical schools such as Vedanta, Buddhism, and Jainism have inspired countless spiritual and philosophical traditions worldwide[1][2]. Practices like yoga and Ayurveda, originating from ancient India, remain popular for their holistic approach to health and wellness[2][3].
Legal and Governance Systems
Rome
The Roman Empire's influence on modern law and governance is vast. The Roman legal system, with its principles of justice and codification of laws, serves as the foundation for many contemporary legal systems, including those of the United States and Europe[2][4]. Roman engineering feats, such as the construction of roads, aqueducts, and the use of concrete, have set standards for modern infrastructure[1][4][8]. The concept of citizenship and civic duty promoted by the Romans is echoed in today's political discourse[4].
Persia
The Persian Empire's centralized administration and extensive trade networks played a crucial role in connecting diverse cultures and economies[2]. Persian art, literature, and architecture have also left a lasting legacy, influencing artistic expressions and cultural exchanges in modern society[2][3].
Contributions to Arts and Culture
Egypt
Ancient Egypt's artistic and architectural achievements have inspired countless artists and architects throughout history. The pyramid form, for instance, continues to influence modern architecture, seen in structures like the Louvre Pyramid in Paris[1][3][7]. Egyptian literature and art provide valuable insights into their culture and beliefs, which continue to captivate contemporary audiences[3][7].
Rome
Roman contributions to art and architecture are profound, with innovations such as the use of arches, domes, and concrete in construction[1][2][4][8]. The Colosseum's design has influenced the structure of modern sports stadiums, and Roman sculpture and frescoes remain admired for their realism and detail[4][8].
Maya and Aztec

The Maya and Aztec civilizations made significant advancements in astronomy, mathematics, and architecture. The Maya calendar, known for its accuracy, has influenced modern timekeeping[1][2]. Their architectural achievements, including the construction of pyramids and cities, display a high level of engineering skill and artistic creativity[1][3].
Conclusion
The contributions of ancient civilizations to modern society are extensive and multifaceted. From technological innovations and agricultural practices to philosophical thought and legal systems, the legacy of these early cultures continues to shape our world. By studying and appreciating these ancient advancements, we gain a deeper understanding of the roots of contemporary society and the enduring impact of human ingenuity and creativity.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
- First Human PhotoIn 1838, Paris's bustling Boulevard du Temple turned ghostly: a lone bootblack, frozen by a 10‐min exposure, proves only the motionless are captured . What still moment defines you?
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Transcript
Imagine a vocoder as a painter combining two signals: one provides the words—the voice modulator—and the other supplies the tone—the synth carrier. The vocoder splits the voice into multiple frequency bands and uses them to shape the synth tone, crafting a striking robotic effect. Hear the transformation in three quick steps: first a dry voice, then a dry synth, and finally the vocoded result where the bands sculpt a new, electrifying sound. For clearer articulation, over-articulate your words so each band captures maximum detail, ensuring your vocoder effect remains crisp and intelligible.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
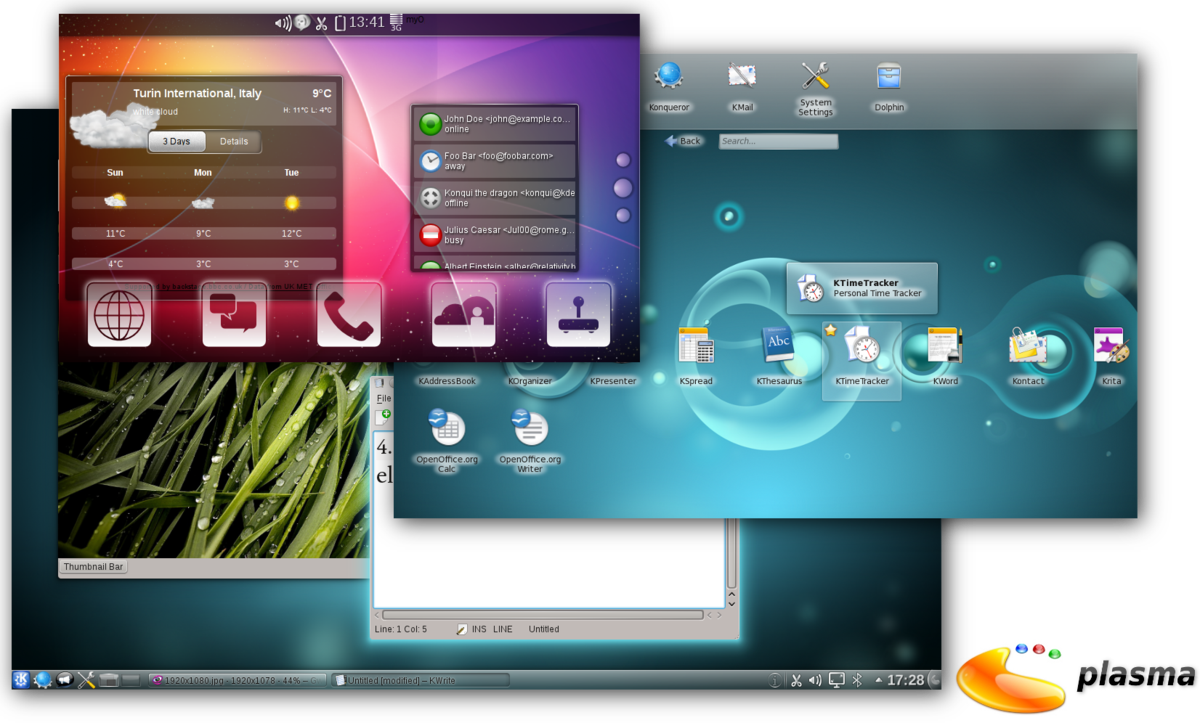
Frutiger Aero visually represents a utopian future through its use of bright colors, particularly blues and greens, which evoke a sense of optimism and tranquility. The aesthetic features clean environments with elements like glossy textures and skeuomorphism, creating a harmonious integration of technology and nature[1]. Imagery often includes serene natural landscapes, suggesting an idealized world where technology coexists with the environment rather than detracting from it[3].
This optimistic portrayal is further enhanced by smooth, user-friendly interfaces characteristic of tech products from the mid-2000s, reflecting a belief in a bright digital future that is both welcoming and accessible[5].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
The Mystery of the Peruvian Rain-Tree: Unraveling the True Cause
In the lush landscapes of the Eastern Peruvian Andes, tales of a remarkable tree that produced its own rain captured the imagination of many in the 19th century. Known locally as Tamia-caspi, or the "Rain-tree," this botanical wonder was rumored to possess the extraordinary ability to draw moisture from the air and shower it onto the ground below. This report examines the historical accounts of this phenomenon, contrasting the popular myth with the scientific explanation that ultimately demystified the weeping tree. The investigation reveals a fascinating symbiotic relationship between flora and fauna, where the true source of the "rain" was not the tree itself, but a multitude of insects.
The Saman Tree (Pithecolobium saman)
A photograph of a Pithecolobium saman, commonly known as a Rain Tree. These large, wide-canopied trees are native to the neotropics and are the type of tree associated with the "raining" phenomenon in Peru.
The Popular Myth: A Self-Watering Wonder
Widespread reports of the Rain-tree gained significant traction around 1877, largely fueled by an account attributed to the United States Consul in Moyobamba, Northern Peru[1]. This narrative described a tree capable of absorbing and condensing atmospheric humidity with what was called "astonishing energy"[1]. According to the story, the tree's process was so efficient that water would constantly ooze from its trunk and drip from its branches in copious amounts[1]. The volume of this supposed precipitation was said to be so great that the ground directly beneath the tree's canopy was transformed into a "perfect swamp"[1].
The tale was not merely a curiosity; it carried practical implications. Proponents of this theory suggested that the Rain-tree could be a solution to agricultural challenges in arid regions. There was a serious proposal to cultivate these trees in the dry coastal areas of Peru, with the hope that they would irrigate the land and benefit local farmers[1]. This captivating story of a self-watering tree presented a seemingly miraculous solution to drought, blending botanical marvel with agricultural promise.
The Scientific Explanation: An Entomological Answer
While the story of the humidity-condensing tree was compelling, a more scientific explanation was provided by Dr. Spruce, a respected traveler with extensive experience in South America[1]. Dr. Spruce confirmed that the Tamia-caspi was indeed a real phenomenon, but not in the way popular rumor described it[1]. He clarified, "The Tamia-caspi, or Rain-tree of the Eastern Peruvian Andes is not a myth, but a fact, although not exactly in the way popular rumour has lately presented it"[1].
Dr. Spruce recounted his own direct observation of the phenomenon, which occurred near Moyobamba in September 1855. On a morning with a completely clear sky, he and his companions walked under a tree from which a "smart rain was falling"[1]. Intrigued, he looked up into the branches to find the true source. His investigation revealed that the 'rain' was not a product of the tree itself. Instead, he observed "a multitude of cicadas, sucking the juices of the tender young branches and leaves, and squirting forth slender streams of limpid fluid"[1].
Cicadas Creating the 'Rain' on a Tree Branch
An illustrative, detailed macro view of several cicadas on a lush green tree branch. The cicadas are shown piercing the bark to suck sap and excreting fine streams of fluid, which fall like a gentle rain, capturing the true cause of the Rain-tree phenomenon. The lighting is bright and natural, as if on a clear day.
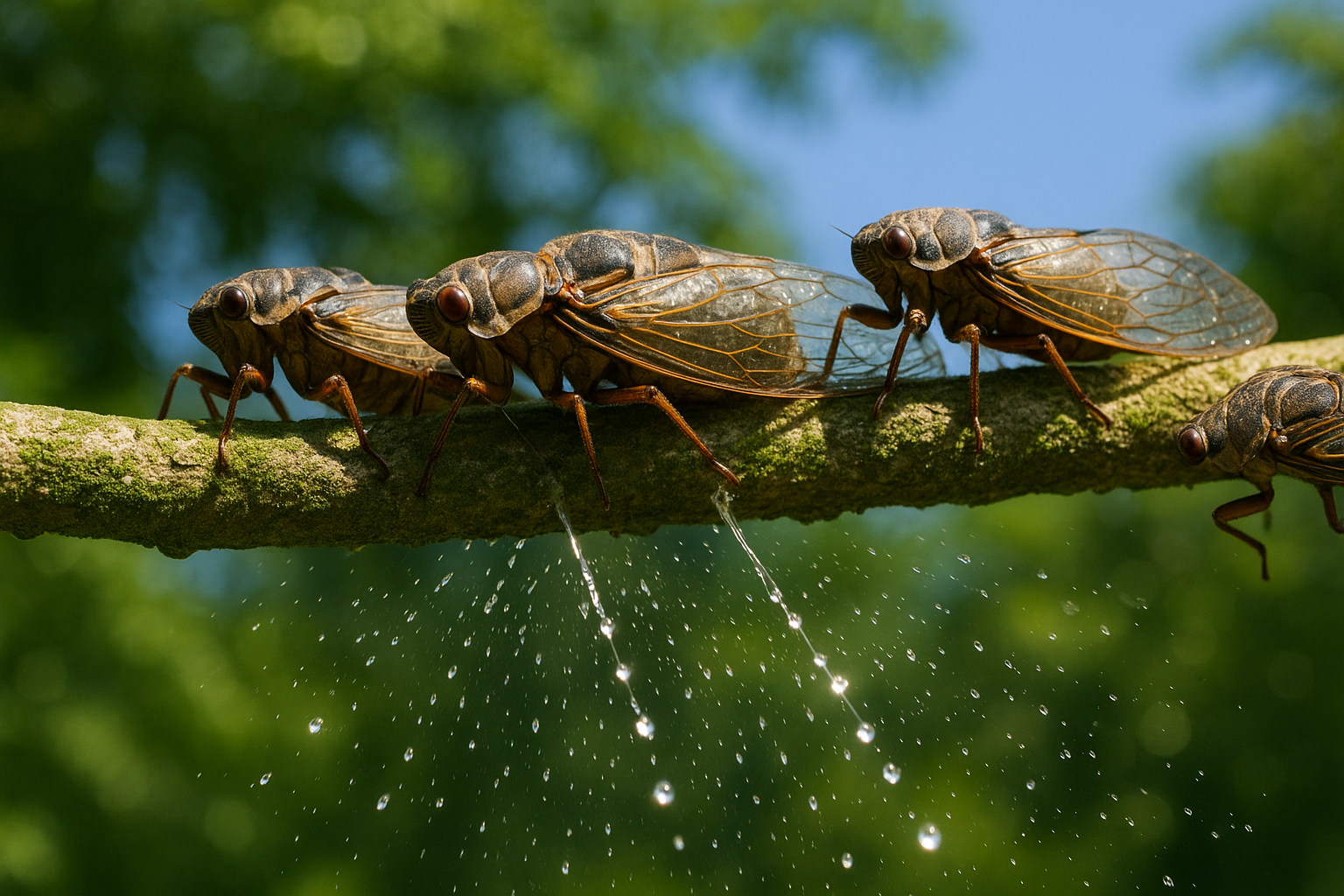

This observation provided the definitive answer. The 'rain' was the excrement, often called honeydew, from a massive number of cicadas feeding on the tree's sap. The insects would consume the nutrient-rich sap and expel the excess water and sugars as a clear liquid. When thousands of cicadas did this simultaneously, the collective discharge created the effect of a continuous shower. Dr. Spruce noted that his Peruvian guides were already well-acquainted with this occurrence, understanding that virtually any tree hosting a large population of feeding cicadas could become a temporary Tamia-caspi[1]. He concluded that while a specific tree might have been famously known for this effect, the cicada was the universal agent responsible for the moisture[1].
Conclusion
The true cause of the "Rain-tree" phenomenon in the Peruvian Andes is not a botanical marvel of atmospheric condensation, but rather a remarkable example of insect biology. The popular 19th-century myth of a tree that could water the earth beneath it was debunked by the careful observations of Dr. Spruce. His firsthand account clarified that the "rain" was, in fact, the collective fluid excretions of a vast number of cicadas feeding on the tree's sap[1]. This scientific explanation replaces a fantastical tale with an equally fascinating natural reality, highlighting the powerful, and sometimes surprising, impact that insects can have on their environment.
References
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
The smallest flowering plant is the little Duckweed.
A Eucalyptus tree can reach a towering height of 420 feet.
The midpoint between the largest and smallest flowering plants is a 20-inch St. John's Wort.
The smallest plant is a single-celled alga, 1/2500th of an inch in diameter.
Including microscopic life, the average plant size is a moss less than an inch-and-a-half tall.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).

It should rather be said that plants acquire and display this power only when it is of advantage to them.
M. C. Cooke[1]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
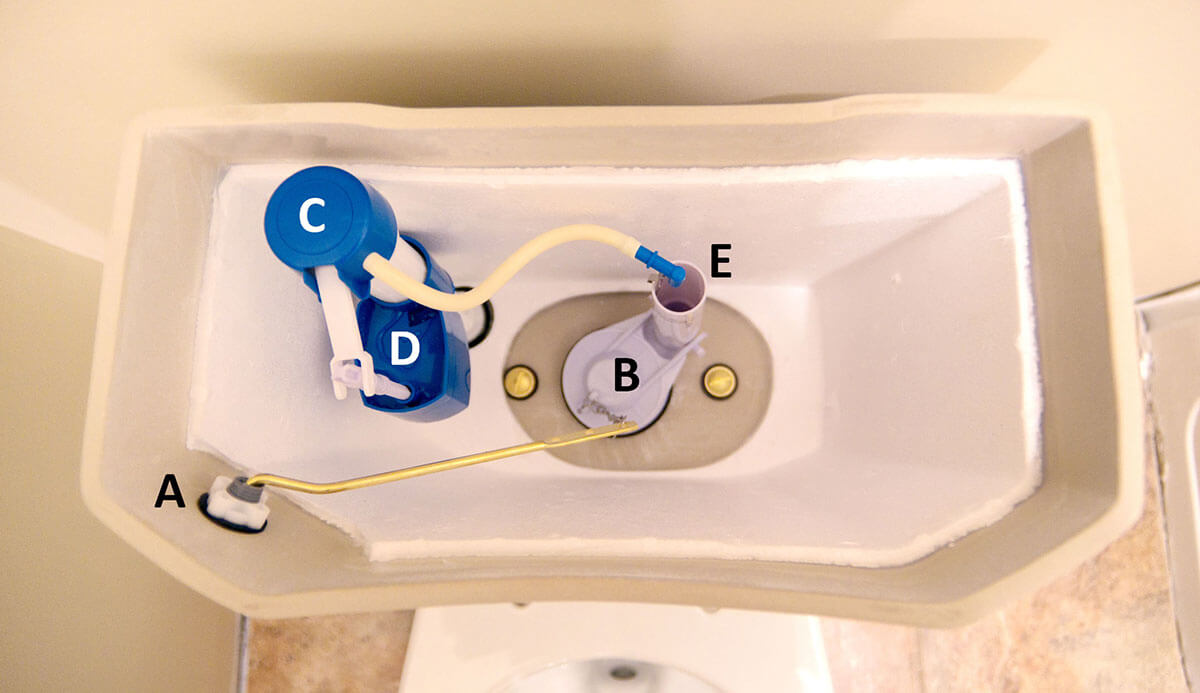


:strip_icc()/bhg-how-to-fix-running-toilet-step-04-0267_3pbsjtfjqEhBksff2NWQ5J-b08fe3c4723d4b29a67a7c8e6af9de50.jpg)

:strip_icc()/bhg-how-to-fix-running-toilet-step-02-0273_7Pr6JFRBK7iBY-aEg3n7Bk-d065d8a4fa604f2c819546e96f03d353.jpg)









