The Mystery of the Peruvian Rain-Tree: Unraveling the True Cause
In the lush landscapes of the Eastern Peruvian Andes, tales of a remarkable tree that produced its own rain captured the imagination of many in the 19th century. Known locally as Tamia-caspi, or the "Rain-tree," this botanical wonder was rumored to possess the extraordinary ability to draw moisture from the air and shower it onto the ground below. This report examines the historical accounts of this phenomenon, contrasting the popular myth with the scientific explanation that ultimately demystified the weeping tree. The investigation reveals a fascinating symbiotic relationship between flora and fauna, where the true source of the "rain" was not the tree itself, but a multitude of insects.
The Saman Tree (Pithecolobium saman)
A photograph of a Pithecolobium saman, commonly known as a Rain Tree. These large, wide-canopied trees are native to the neotropics and are the type of tree associated with the "raining" phenomenon in Peru.
The Popular Myth: A Self-Watering Wonder
Widespread reports of the Rain-tree gained significant traction around 1877, largely fueled by an account attributed to the United States Consul in Moyobamba, Northern Peru[1]. This narrative described a tree capable of absorbing and condensing atmospheric humidity with what was called "astonishing energy"[1]. According to the story, the tree's process was so efficient that water would constantly ooze from its trunk and drip from its branches in copious amounts[1]. The volume of this supposed precipitation was said to be so great that the ground directly beneath the tree's canopy was transformed into a "perfect swamp"[1].
The tale was not merely a curiosity; it carried practical implications. Proponents of this theory suggested that the Rain-tree could be a solution to agricultural challenges in arid regions. There was a serious proposal to cultivate these trees in the dry coastal areas of Peru, with the hope that they would irrigate the land and benefit local farmers[1]. This captivating story of a self-watering tree presented a seemingly miraculous solution to drought, blending botanical marvel with agricultural promise.
The Scientific Explanation: An Entomological Answer
While the story of the humidity-condensing tree was compelling, a more scientific explanation was provided by Dr. Spruce, a respected traveler with extensive experience in South America[1]. Dr. Spruce confirmed that the Tamia-caspi was indeed a real phenomenon, but not in the way popular rumor described it[1]. He clarified, "The Tamia-caspi, or Rain-tree of the Eastern Peruvian Andes is not a myth, but a fact, although not exactly in the way popular rumour has lately presented it"[1].
Dr. Spruce recounted his own direct observation of the phenomenon, which occurred near Moyobamba in September 1855. On a morning with a completely clear sky, he and his companions walked under a tree from which a "smart rain was falling"[1]. Intrigued, he looked up into the branches to find the true source. His investigation revealed that the 'rain' was not a product of the tree itself. Instead, he observed "a multitude of cicadas, sucking the juices of the tender young branches and leaves, and squirting forth slender streams of limpid fluid"[1].
Cicadas Creating the 'Rain' on a Tree Branch
An illustrative, detailed macro view of several cicadas on a lush green tree branch. The cicadas are shown piercing the bark to suck sap and excreting fine streams of fluid, which fall like a gentle rain, capturing the true cause of the Rain-tree phenomenon. The lighting is bright and natural, as if on a clear day.
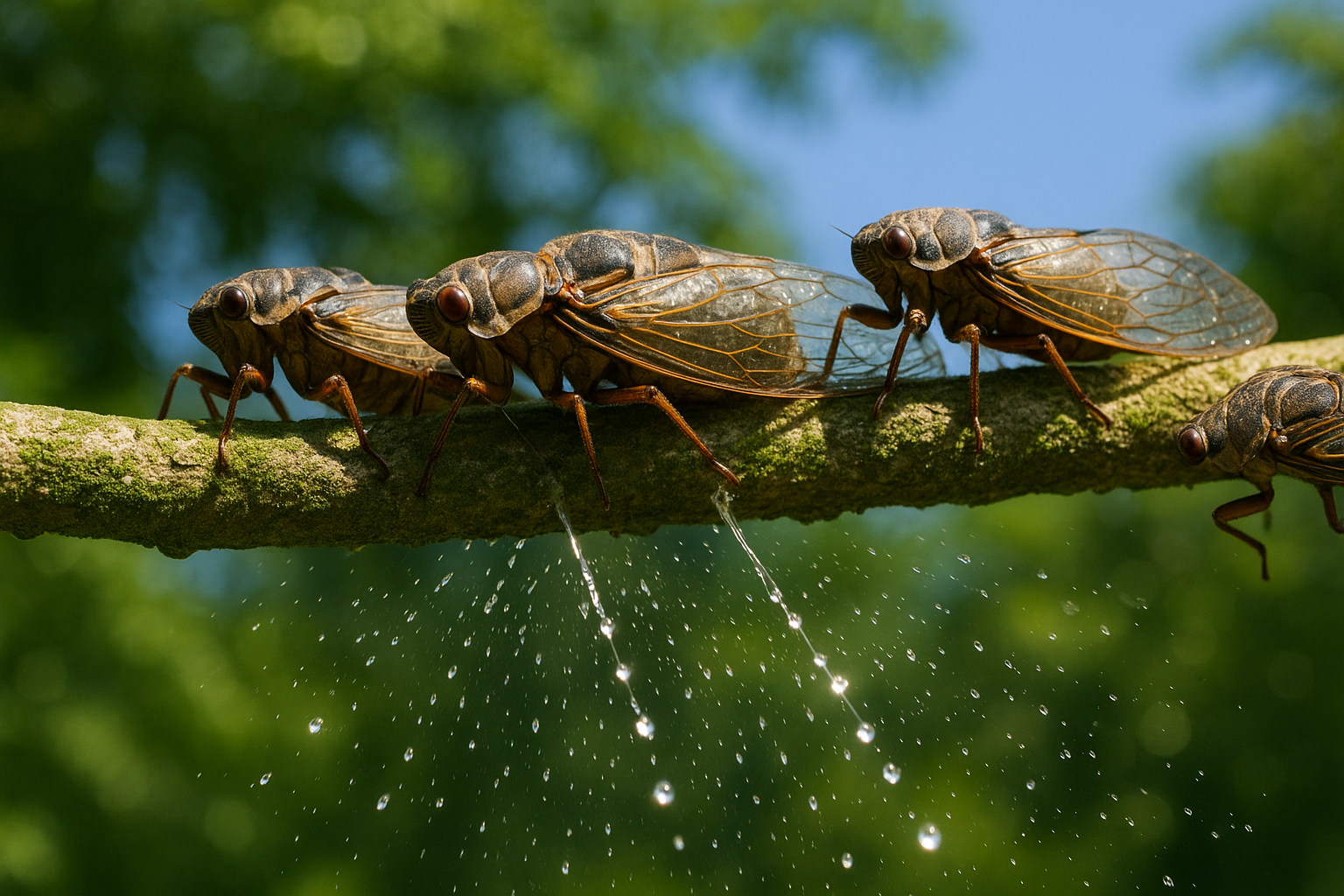

This observation provided the definitive answer. The 'rain' was the excrement, often called honeydew, from a massive number of cicadas feeding on the tree's sap. The insects would consume the nutrient-rich sap and expel the excess water and sugars as a clear liquid. When thousands of cicadas did this simultaneously, the collective discharge created the effect of a continuous shower. Dr. Spruce noted that his Peruvian guides were already well-acquainted with this occurrence, understanding that virtually any tree hosting a large population of feeding cicadas could become a temporary Tamia-caspi[1]. He concluded that while a specific tree might have been famously known for this effect, the cicada was the universal agent responsible for the moisture[1].
Conclusion
The true cause of the "Rain-tree" phenomenon in the Peruvian Andes is not a botanical marvel of atmospheric condensation, but rather a remarkable example of insect biology. The popular 19th-century myth of a tree that could water the earth beneath it was debunked by the careful observations of Dr. Spruce. His firsthand account clarified that the "rain" was, in fact, the collective fluid excretions of a vast number of cicadas feeding on the tree's sap[1]. This scientific explanation replaces a fantastical tale with an equally fascinating natural reality, highlighting the powerful, and sometimes surprising, impact that insects can have on their environment.
References
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
The smallest flowering plant is the little Duckweed.
A Eucalyptus tree can reach a towering height of 420 feet.
The midpoint between the largest and smallest flowering plants is a 20-inch St. John's Wort.
The smallest plant is a single-celled alga, 1/2500th of an inch in diameter.
Including microscopic life, the average plant size is a moss less than an inch-and-a-half tall.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

It should rather be said that plants acquire and display this power only when it is of advantage to them.
M. C. Cooke[1]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Transcript
Did you know that some plants behave a lot like animals? A book called Freaks and Marvels of Plant Life explores the incredible and sometimes bizarre world of vegetation, revealing plants that hunt, move, and have other amazing abilities. Take the little Sundew plant, for example. Its leaves are covered in sticky, sparkling tentacles. When an insect lands on them, the tentacles bend over, trapping the bug. The plant then releases an acid, much like an animal's stomach, to dissolve and digest its meal! Then there is the famous Venus's Fly-trap, which one scientist compared to a rat-trap. Its leaves snap shut in an instant when an insect touches tiny trigger hairs inside, squeezing its prey to death before digesting it. It makes you wonder, does it not? If some plants can eat meat, what other amazing secrets is the plant kingdom hiding?
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Freaks and Marvels: A Victorian Exploration of Botanical Wonders
Published in 1882, M. C. Cooke's Freaks and Marvels of Plant Life; Or, Curiosities of Vegetation serves as a fascinating window into the Victorian-era popularization of science[1]. The book's primary objective was to present the remarkable phenomena of the vegetable kingdom to a general audience, deliberately avoiding dense technical jargon[1]. By collecting and explaining curious facts about plant structure, habits, and behaviors, Cooke aimed to stimulate a broader interest in the study of botany[1]. The work heavily draws upon the groundbreaking research of contemporary scientists, most notably Charles Darwin, translating their complex findings into an accessible narrative for readers who might otherwise be deterred by purely scientific texts[1].
The scope of the book is extensive, moving from the microscopic to the gigantic. The introduction alone touches upon the vast diversity of plant species and their practical benefits to humanity, such as the purported use of Eucalyptus and sunflowers in mitigating malaria[1]. This report will summarize the key topics and extraordinary plant behaviors detailed in Cooke's work, covering carnivorous plants, complex plant movements, methods of seed dispersal, and the cultural significance of certain species.
The World of Carnivorous Plants
A significant portion of the book is dedicated to the astonishing world of carnivorous plants, which capture and digest insects and other small creatures. Cooke details the intricate mechanisms these plants have evolved to supplement their nutrition, effectively blurring the line between the animal and vegetable kingdoms.
- The Sundews (Drosera): These plants are characterized by leaves covered in glandular hairs, often called 'tentacles,' which exude a sticky, dew-like fluid[1]. When an insect becomes ensnared, the surrounding tentacles slowly bend inward. The glands then secrete an acidic fluid that dissolves the animal matter, allowing the plant to absorb the nutrients[1].
- Venus's Fly-trap (Dionæa): Described as an 'American cousin' of the Sundew, the Venus's Fly-trap possesses a more dramatic trapping mechanism[1]. Its leaf consists of two hinged lobes that can snap shut. When an insect touches the sensitive trigger hairs on the leaf's surface, the lobes collapse with enough force to prevent the prey's escape[1]. Following capture, the plant secretes a fluid similar to gastric juice to digest its victim[1].
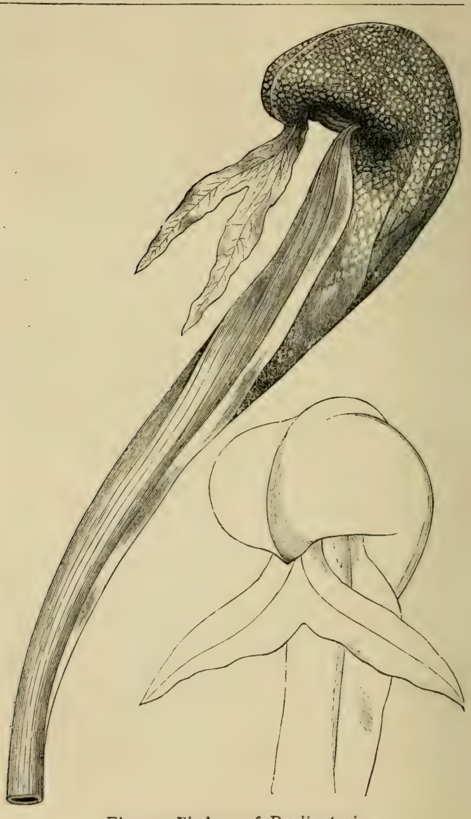
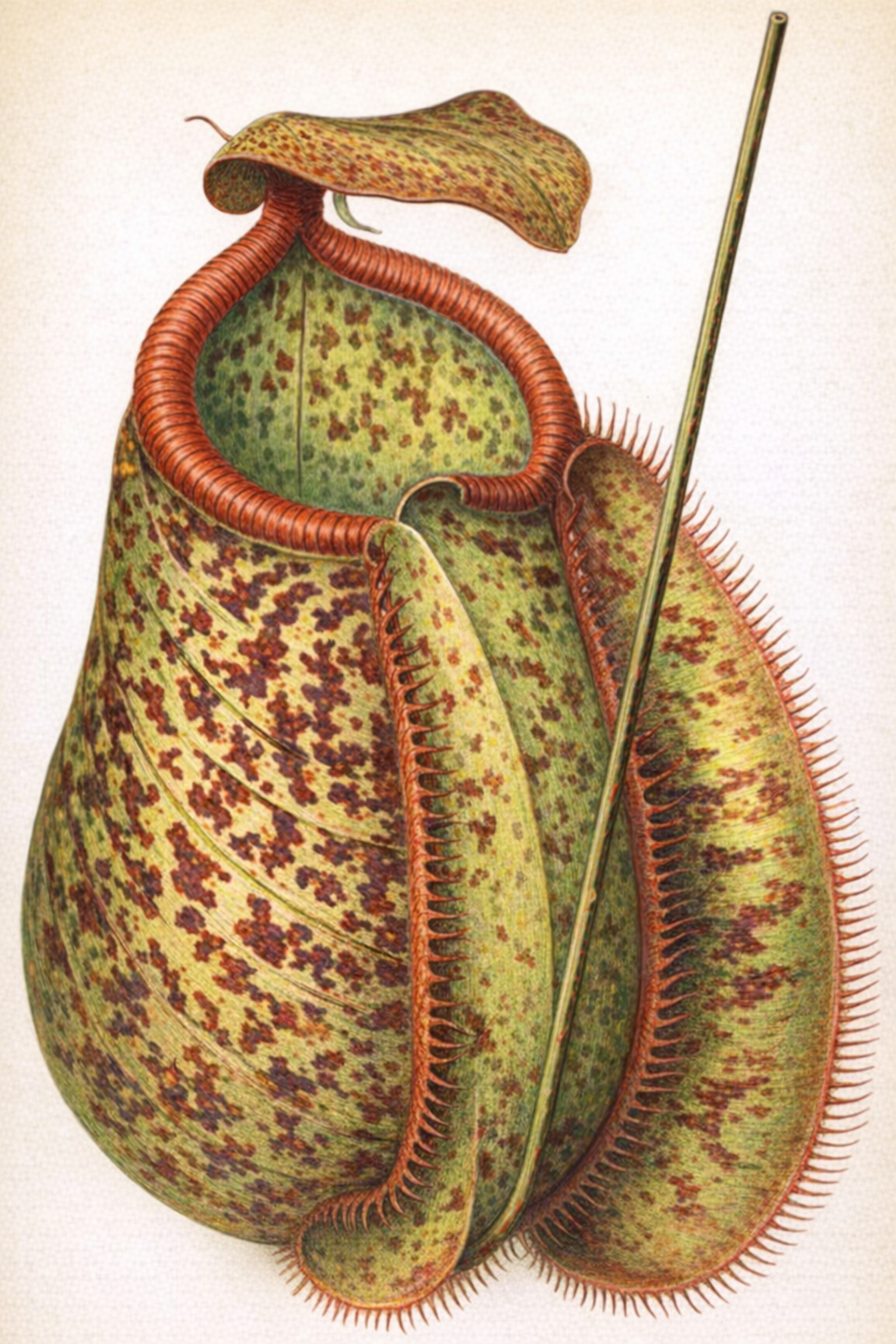
- Pitcher-Plants (Sarracenia, Nepenthes, etc.): This group uses modified leaves shaped into pitchers, trumpets, or urns to trap prey[1]. Insects are often attracted to the pitcher's mouth by a sweet nectar. Once they venture inside, they lose their footing and fall into the fluid below. Downward-pointing hairs line the pitcher's inner walls, making escape nearly impossible[1]. The plant then absorbs nutrients from the decaying or digested bodies of its captives[1].
Pitchers of Darlingtonia
An illustration from the book showing the unique, hooded pitchers of the Darlingtonia, or Cobra Lily, a type of carnivorous plant native to North America.
Pitcher of Nepenthes Chelsoni
This image displays the intricate structure of a Nepenthes pitcher, highlighting the specialized leaf modification used to trap insects.
The Power of Movement in Plants
Cooke also explores the various forms of motion exhibited by plants, challenging the static perception of the vegetable world. These movements, though often slow, are crucial for growth, support, and survival.
- Gyration and Circumnutation: The book highlights the discovery that nearly every growing part of a plant is in a state of constant, subtle rotation[1]. This movement, observed in stems, roots, and leaves, is a fundamental aspect of plant growth[1].
- Heliotropism and the Compass-Plant: The text discusses the common phenomenon of plants turning towards a light source (heliotropism) and its opposite[1]. It also describes the American 'Compass-plant,' which was reputed to align its leaves along a north-south axis, acting as a natural compass[1].
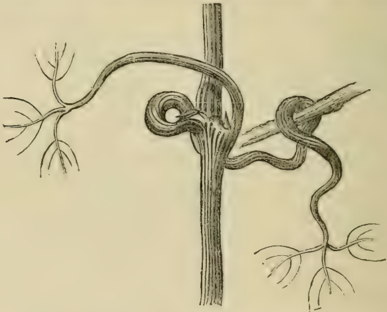
- Twiners and Climbers: The mechanics of climbing plants are explained in detail. A twining shoot, like that of a hop, revolves in the air until it makes contact with a support. The point of contact is arrested while the free end continues to rotate, causing the shoot to wind itself around the object[1]. Other plants use sensitive leafstalks (petioles) or specialized tendrils that contract upon contact to grasp supports[1].
- Sensitive and Sleeping Plants: The book covers plants with rapid, touch-induced movements, such as the Mimosa pudica, which folds its leaflets upon being disturbed[1]. It also delves into the 'sleep' of plants (nyctinasty), where leaves change their position at night. This behavior is theorized to protect the leaves' upper surfaces from excessive cooling due to radiation[1].
The Twining Polygonum
An illustration depicting Polygonum convolvulus, a common twining plant, demonstrating the climbing mechanism described in the book.

Other Botanical Curiosities and Marvels
Beyond carnivory and movement, the book presents a wide array of other fascinating botanical subjects, showcasing the diversity of form and function in the plant kingdom.
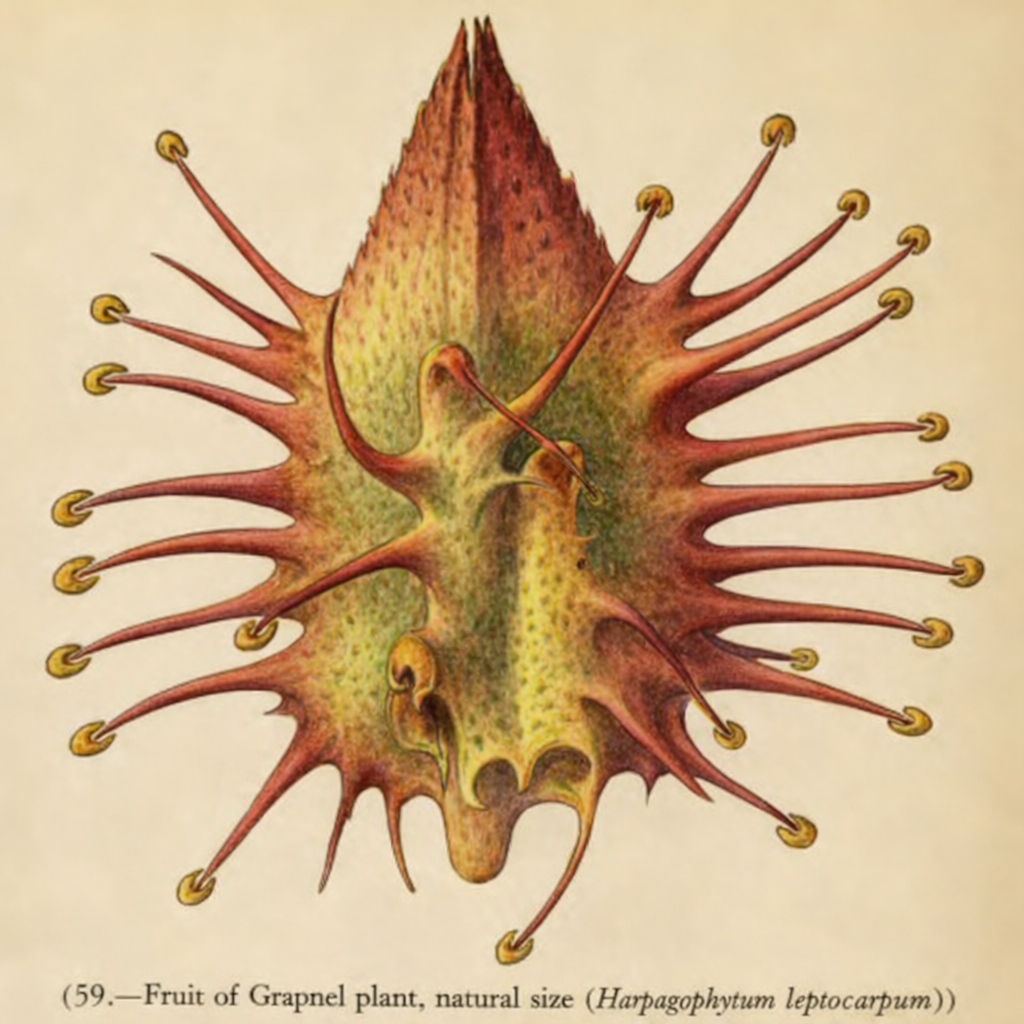
- Ingenious Seed Dispersal: Cooke describes various strategies plants use to spread their seeds. These include fruits that burst open with explosive force, like the 'squirting cucumber'; seeds equipped with wings or parachutes for wind dispersal, such as the dandelion; and fruits armed with hooks or burrs that attach to the fur of passing animals for transport[1].
- Mimicry in Plants: The text points out remarkable instances of mimicry, where one plant species evolves to resemble another. Examples include African Euphorbias that look strikingly similar to American Cacti, and the flowers of an Australian plant (Actinotus) that imitate the appearance of common daisies[1][1].
- Giants of the Vegetable World: This section is devoted to the largest known plants. It features the towering Sequoia of California and the Eucalyptus of Australia, with one reported specimen reaching a height of 480 feet[1]. Also mentioned are the massive Rafflesia flower, which can be a yard in diameter, and the enormous floating leaves of the Victoria regia water-lily[1].
- Temperature and Luminosity: The book touches on the phenomena of heat generation during the flowering process, especially in the Arum family. It also examines reports of flowers that emit faint flashes of light on warm evenings, as well as the well-known phosphorescence of decaying wood and certain fungi[1].
Fruit of the Grapnel Plant
This illustration shows the hooked fruit of the Grapnel plant (Harpagophytum), a prime example of seed dispersal via attachment to animals.
Mystic, Historic, and Symbolic Flora
The final chapters of the book delve into the rich tapestry of folklore, mythology, and symbolism surrounding certain plants[1]. Cooke explores how species like the mandrake, with its human-shaped root, and the sacred mistletoe have captured the human imagination for centuries. The passion flower is examined for its complex floral structure, which was interpreted by early missionaries as symbolizing the Passion of Christ. The book concludes by discussing the national floral emblems of the British Isles: the rose for England, the thistle for Scotland, and the shamrock for Ireland, connecting botany with cultural identity.
Female Mandrake
A historical depiction of a female mandrake, illustrating the anthropomorphic qualities attributed to the plant's root, which fueled centuries of folklore and superstition.

Male Mandrake with Dog
This illustration shows a male mandrake and references the legend that a dog had to be used to pull the plant from the ground to avoid its fatal scream.

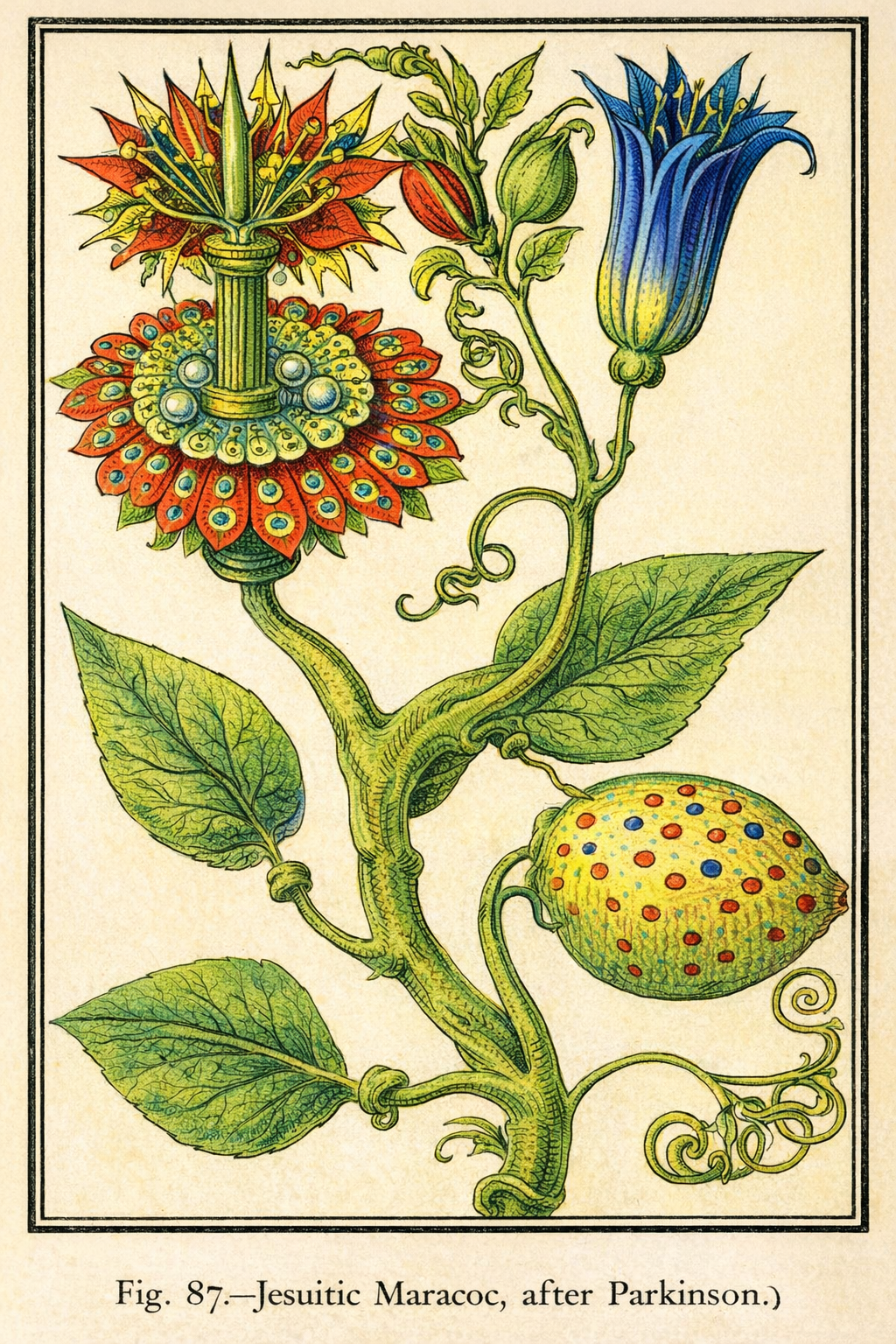
The Passion Flower (Jesuitic Maracoc)
An illustration of the Passion Flower, so named because its intricate parts were seen by Christian missionaries as symbols of the crucifixion of Jesus.

Conclusion
M. C. Cooke's Freaks and Marvels of Plant Life stands as a testament to the Victorian era's passion for natural history and the desire to share scientific knowledge with a wider public. By focusing on the most curious, dramatic, and seemingly bizarre aspects of the plant world, from insect-eating leaves to moving flowers, Cooke successfully created a work that was both educational and highly entertaining. The book not only summarized the cutting-edge botanical research of its time but also fostered a sense of wonder and appreciation for the intricate and often surprising lives of plants.
References
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).

Aman had toenter the lists resolved toconquer ordie: seeing that bythose aforesaid Danish andLombard laws theconqueror didjust what hepleased with hisunsuccessful opponent
Unknown[1]
If you were sofortunate astokillyour opponent, ought youtoburn hisbody orletthe family bury it? Could a“second”make avalid surrender forhisprincipal?
Unknown[1]

The question—even thequestion ofchivalry, the defence ofthehonour offair ladies—resolved itself into afew cut-and-dried formulas.
Unknown[1]
Every one,weunderstand, wasbound todefend thecharacter ofthefairsexwhatever hemight happen tothink orknow.
Unknown[1]
Late inlife, aswelearn from theopening pages of theRodomontades Espagnolles, hewas foralong period disabled byafallfrom awhite horse
Unknown[1]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).