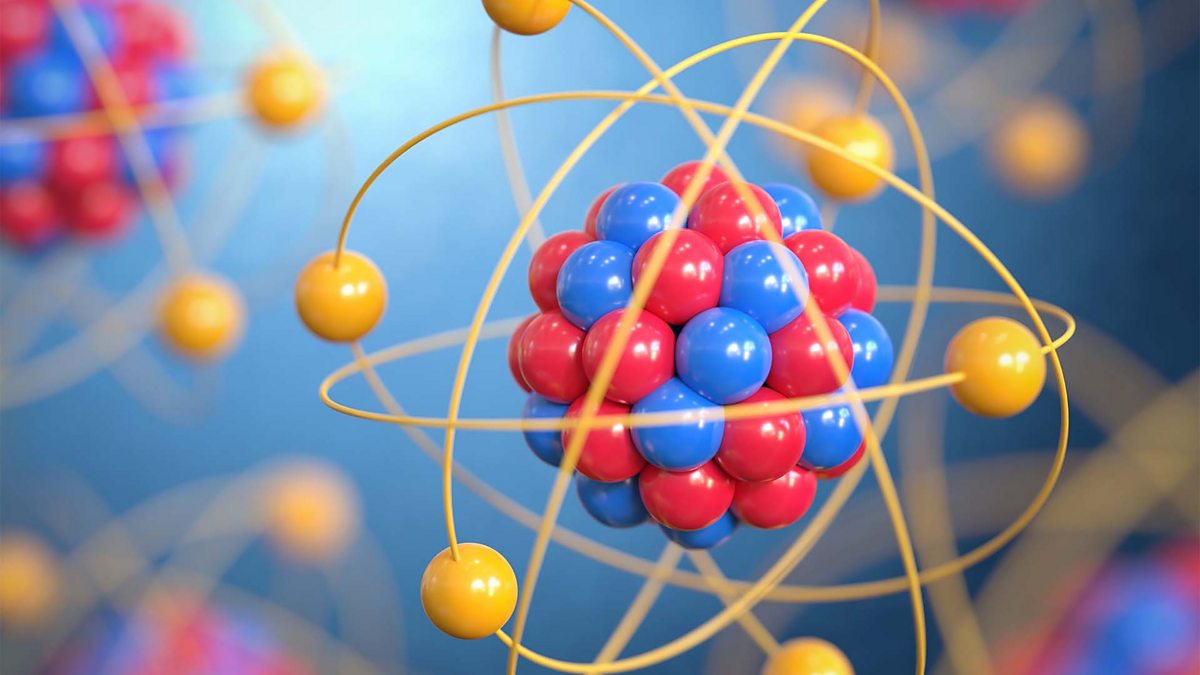
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of a chemical element. It consists of a central nucleus made up of protons, which carry a positive charge, and neutrons, which are neutral. Electrons, which have a negative charge, orbit the nucleus in designated energy levels called electron shells. Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus, while the electrons orbit far away, making the atom predominantly empty space[1][4][5].
The atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus, determines the element's identity. In a stable, neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons, resulting in no net charge[2][6].
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).