
The advent of autonomous vehicles (AVs) presents a potential paradigm shift in transportation, bringing with it a mixture of enthusiasm for innovation and apprehension about societal impacts. A thorough examination of the advantages and disadvantages reveals nuances that merit close attention.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
Safety Improvements

A fundamental advantage of autonomous vehicles is their capacity to reduce traffic accidents, as they remove human error—the leading cause of over 90% of road accidents. High-precision sensors and advanced algorithms enable AVs to respond to immediate surroundings more effectively than human drivers. It has been suggested that fully autonomous vehicles could significantly lower traffic-related fatalities by minimizing driver-related issues such as fatigue and distraction, which account for numerous incidents on the roads[3][6][11].
Increased Mobility and Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles promise greater mobility for individuals who cannot drive due to disabilities, age, or other factors. By providing independent transportation options, AVs can free such individuals from dependence on public transport or others, thus improving their quality of life[1][4][10]. The convenience of AVs may also attract users from various demographics, extending their potential utility across urban and rural communities.
Reduced Traffic Congestion
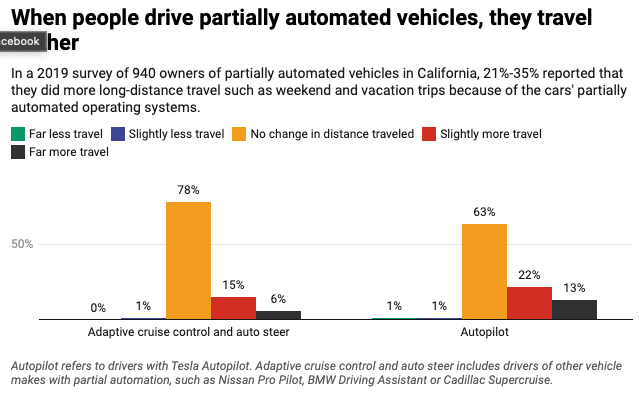
The introduction of AVs could lead to smarter traffic management and decreased congestion. Connected AVs are capable of communication with each other and infrastructure, allowing for optimized routes and more efficient use of road space. This interconnectedness can significantly reduce stop-and-go traffic and encourage more fluid flow, potentially decreasing overall travel times[6][10].
Environmental Benefits

When properly integrated, AVs have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions considerably. Many current AV technologies are being developed with electric propulsion, which can lead to lower fuel consumption. Advanced driving algorithms designed for eco-driving can further enhance energy efficiency, resulting in decreased environmental footprints[1][5][8]. Some models predict that the overall energy use and emissions could drop substantially as AVs gain traction alongside the transition to renewable energy sources[11].
Land Use Optimization
The shift toward autonomous vehicles may redefine urban landscapes by decreasing the need for extensive parking infrastructure. As AVs can drop passengers off and park themselves in remote locations, urban areas may repurpose parking spaces for green areas or housing, potentially revitalizing city environments[12][3].
Drawbacks of Autonomous Vehicles
Job Displacement
A major concern surrounding the mass adoption of autonomous vehicles is their potential to displace millions of jobs within the driving industry. Professions such as taxi, truck, and delivery drivers face significant threats from automation, as companies may opt for AVs to cut costs associated with human labor. This employment shift could exacerbate economic inequalities and challenge workers to find alternative employment opportunities[9][10][12].
Liability and Legal Challenges
The rise of AVs introduces complex liability questions regarding accidents. Determining responsibility—whether it lies with the vehicle owner, manufacturer, or software developer—remains unresolved. This ambiguity could lead to significant legal disputes and challenges for the insurance industry, which is currently grappling with the implications of automated driving technology[6][10][9].
Cybersecurity Risks
As AVs rely heavily on software and connectivity, they may be susceptible to cyberattacks. Hackers gaining control of AV systems pose a serious risk, as compromised vehicles could be turned against their passengers or used in malicious activities[8][9]. The extensive data collection required to operate AVs also raises privacy concerns, particularly regarding how personal information is stored and used.
Environmental Considerations
While there is potential for reduced emissions from autonomous electric vehicles, there are caveats. If the energy sources used to charge these vehicles remain non-renewable, their environmental benefits could be undermined. Moreover, increased convenience may encourage longer commutes and higher overall vehicle miles traveled, potentially leading to greater energy consumption and emissions overall[11][12].
Uncertain Public Acceptance
Finally, despite the technological advances, a significant portion of the public remains skeptical about fully autonomous vehicles. Factors contributing to this hesitance include fears over safety and a lack of understanding regarding the technology’s capabilities and limitations. Effective public education and trust-building will be essential to facilitate the wider acceptance of AVs in society[9].
Conclusion
The development of autonomous vehicles holds enormous promise, poised to revolutionize transportation through enhanced safety, accessibility, and efficiency. However, it also presents serious challenges that society must navigate, such as job displacement, liability questions, and cybersecurity risks. As this technology continues to evolve, ongoing discourse and innovative policy-making will be necessary to maximize benefits and mitigate drawbacks. The balance struck between these competing interests will ultimately shape the future landscape of mobility.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).