
Introduction
Space exploration continues to push the boundaries of scientific discovery and technological advancement. The latest missions not only expand our knowledge of the cosmos but also contribute to practical applications on Earth. This report synthesizes details from recent missions and public opinions to provide insights into their implications.
Recent Space Exploration Highlights
International Space Station (ISS) Research
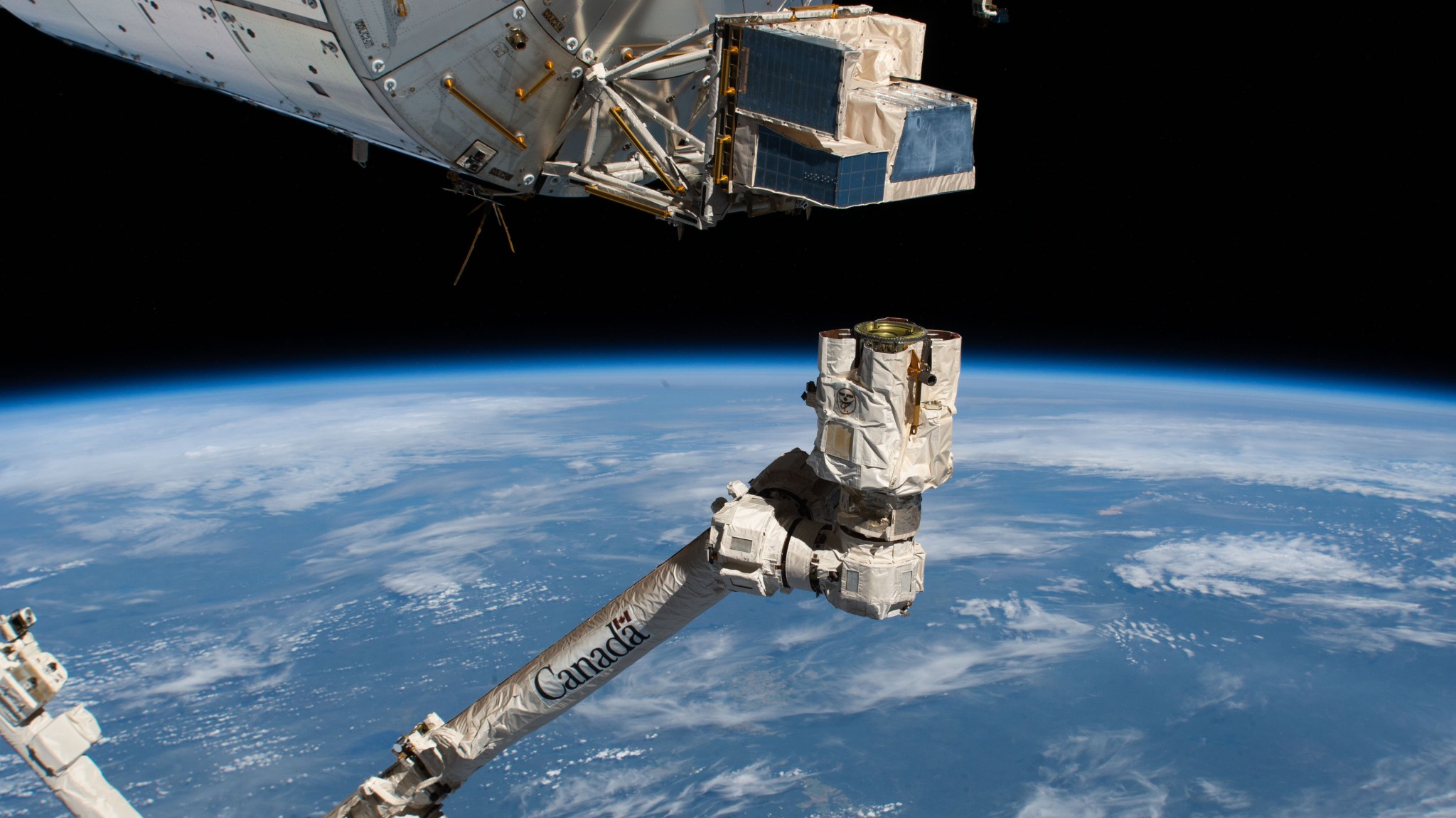

The International Space Station continues to be a hub for groundbreaking technology demonstrations and scientific investigations. Over 3,700 investigations have been conducted, resulting in over 4,000 research articles. Key research projects include the Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) and the Atmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor (ASIM), which study neutron star structures and upper-atmospheric discharges respectively[2].
SpaceX Missions
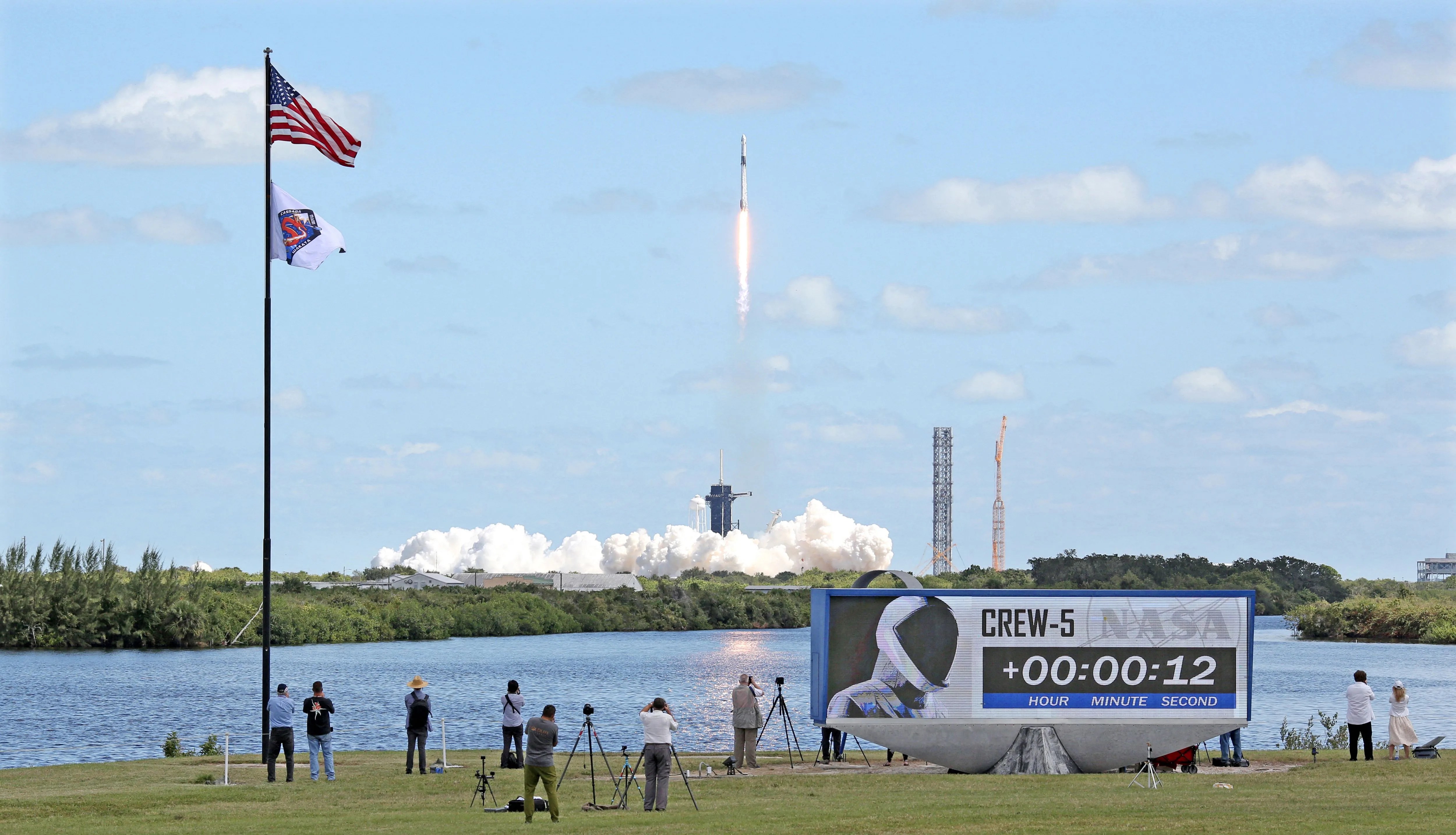

SpaceX remains at the forefront of commercial space missions. The company recently performed static fire tests on its Falcon 9 rockets in preparation for various missions, including the Starlink satellite launches and the Polaris Dawn mission. The Crew-9 mission is also on the horizon, aiming to transport NASA astronauts and a Roscosmos cosmonaut to the ISS for a six-month stay[1][5][9].
Technological Innovations
Additive Manufacturing
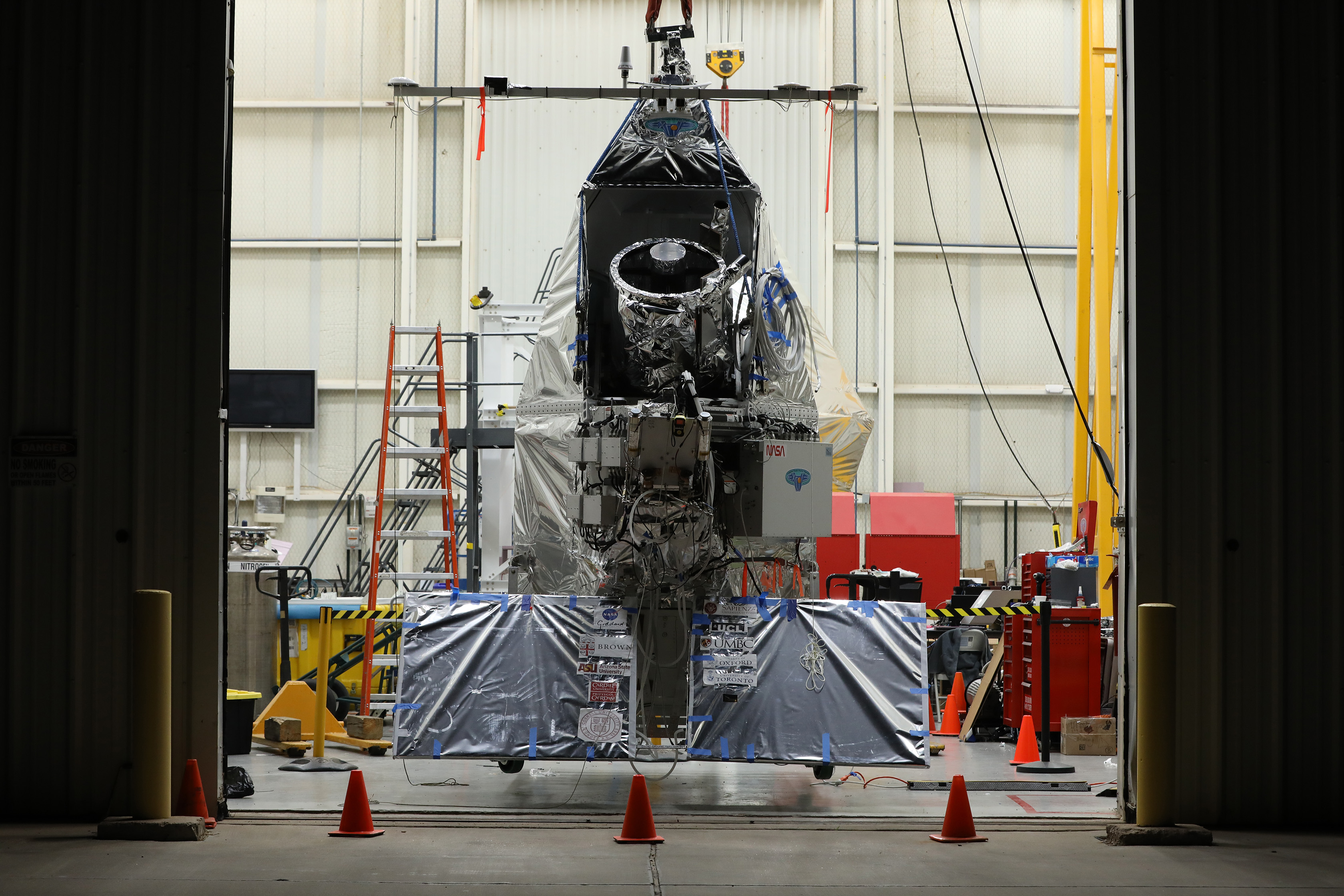

NASA's Rapid Analysis and Manufacturing Propulsion Technology (RAMPT) project has been a game-changer for additive manufacturing in space exploration. The project aims to create stronger, lighter materials for rocket parts, significantly reducing costs and manufacturing times. NASA's partnerships with private companies and academic institutions have facilitated the commercialization of these technologies, fostering a thriving space infrastructure[3].
Materials Science and Industrial Applications
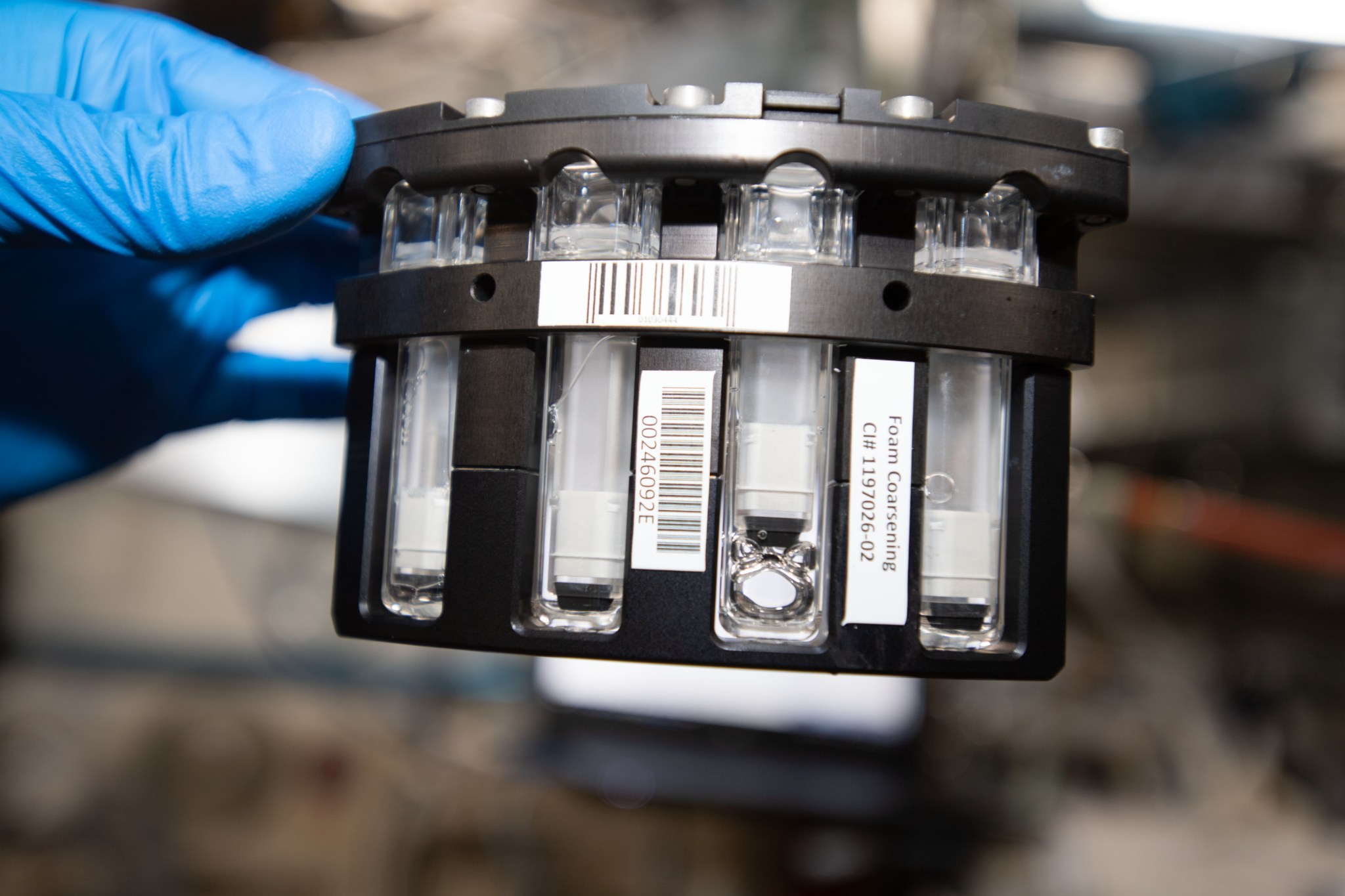

The Electromagnetic Levitator and the Electrostatic Levitation Furnace aboard the ISS are revolutionizing materials science. These facilities allow scientists to study the physical properties of alloys and other materials in microgravity, leading to advancements in 3D printing and the development of new, reliable materials for both space and terrestrial applications[4][8].
Space Tourism and Public Perception
Public Opinion on Space Exploration
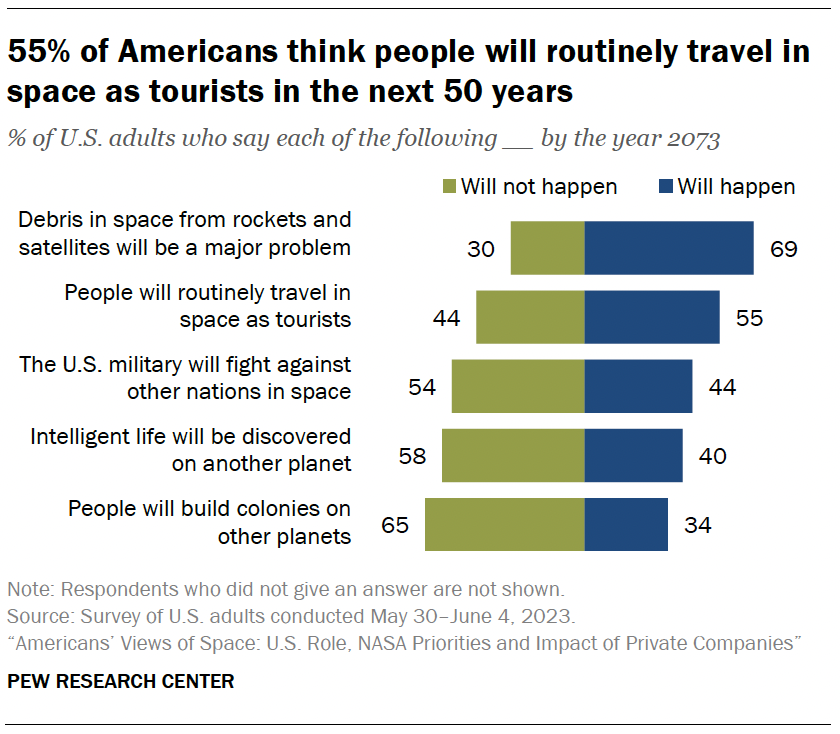
A recent Pew Research Center survey revealed that 55% of Americans expect routine space tourism to become a reality in the next 50 years. Most Americans continue to see NASA as essential for space exploration, despite the increasing involvement of private companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin. Interestingly, there is less public enthusiasm for sending human astronauts to the Moon or Mars compared to other objectives like monitoring asteroids and studying Earth's climate[6].
Private Space Missions

The Polaris Dawn mission, set to achieve the highest Earth orbit by a crewed spacecraft and conduct the first private spacewalk, exemplifies the growing role of private companies in space exploration. Funded and commanded by billionaire Jared Isaacman and operated by SpaceX, this mission aims to advance scientific research and human health, proving that private ventures can complement governmental efforts in space[5][9].
Scientific and Societal Implications
Advances in Scientific Knowledge
Recent missions have provided significant insights into various scientific fields. For instance, NICER's study of pulsars enhances our understanding of gravitational waves, while ASIM's observations improve climate models. These advancements have practical applications, such as better weather prediction and novel disease treatments derived from tissue regeneration studies conducted in microgravity[2].
Broader Applications on Earth
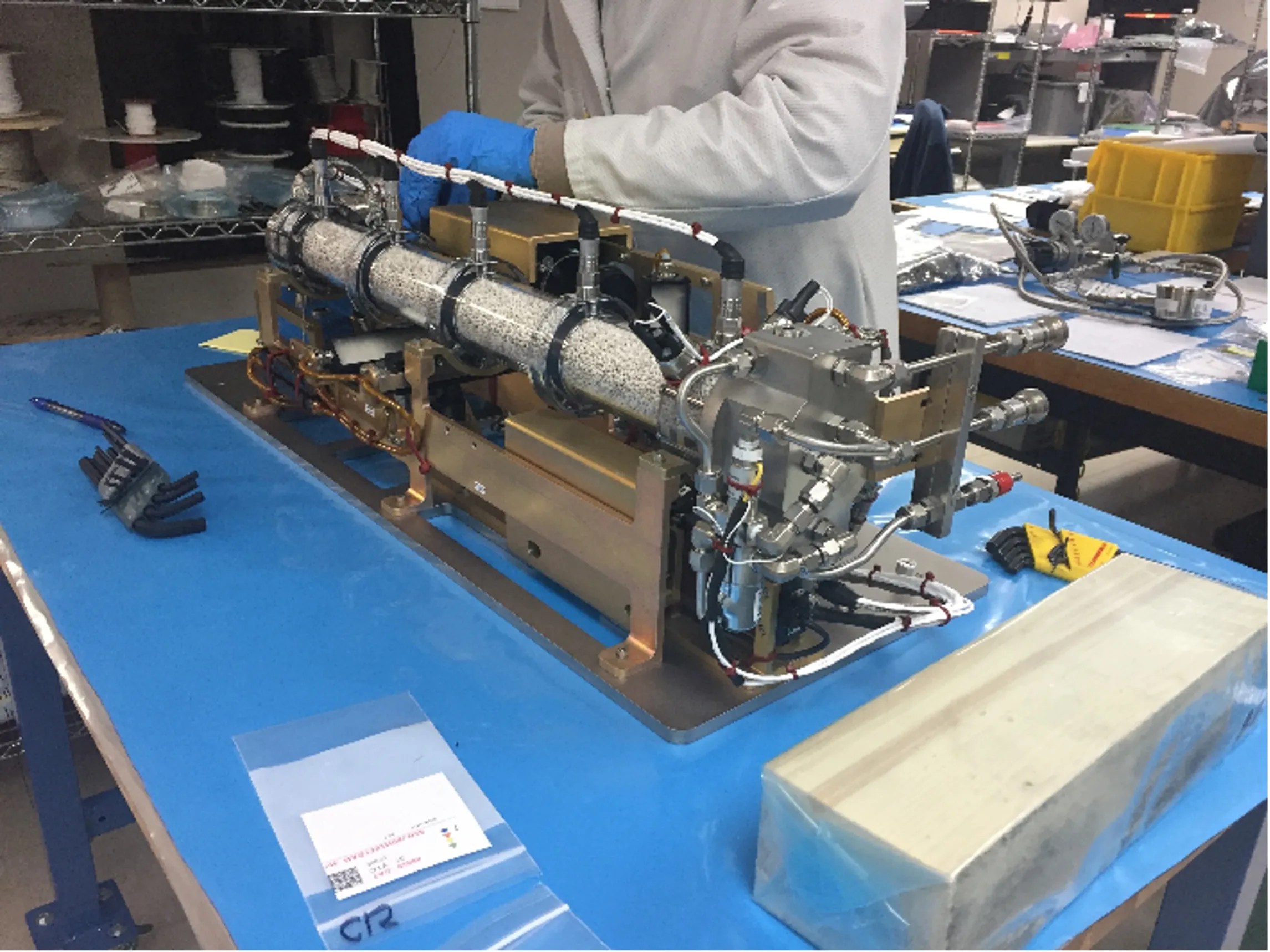

Technologies developed for space missions often find applications on Earth. For example, the outcomes of the Packed Bed Reactor Experiment for water purification have potential uses in improving life support systems in space and water treatment processes on Earth. Similarly, the study of how microgravity affects plant growth could pave the way for sustainable agriculture in harsh environments[8].
Long-term Goals and Collaboration

As countries like China and India ramp up their space activities, international collaboration in space exploration becomes increasingly essential. Missions like those facilitated by the ISS and public-private partnerships exemplify how shared goals can lead to remarkable achievements. The Artemis missions, which aim to return humans to the Moon and eventually Mars, underline the importance of global cooperation[6].
Conclusion
The latest space exploration missions have far-reaching implications, from technological innovations and scientific discoveries to societal benefits and international collaboration. As NASA and private companies continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, these missions not only expand our understanding of the universe but also bring practical, life-enhancing technologies back to Earth. The collaborative efforts in space exploration, supported by public opinion and advanced by scientific research, promise a future where space becomes an integral part of human progress.
This report integrates information from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive overview of the implications of recent space exploration missions. Each section is supported by specific details cited from the texts to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Sources:
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).