Sleep and Cognitive Performance
Sleep plays a critical role in various aspects of cognitive function, significantly influencing attention, memory, emotional regulation, and overall work performance. Research indicates that a lack of sufficient sleep can lead to cognitive impairments that directly impact productivity at work. Poor sleep quality can lead to short-term deficits in intellectual performance and safety risks, such as drowsy driving and decreased motor skills. Additionally, people who experience sleep deprivation often find it difficult to maintain focus and may struggle with memory retention and creative thinking, which can impede their ability to perform well in professional settings[2][4].
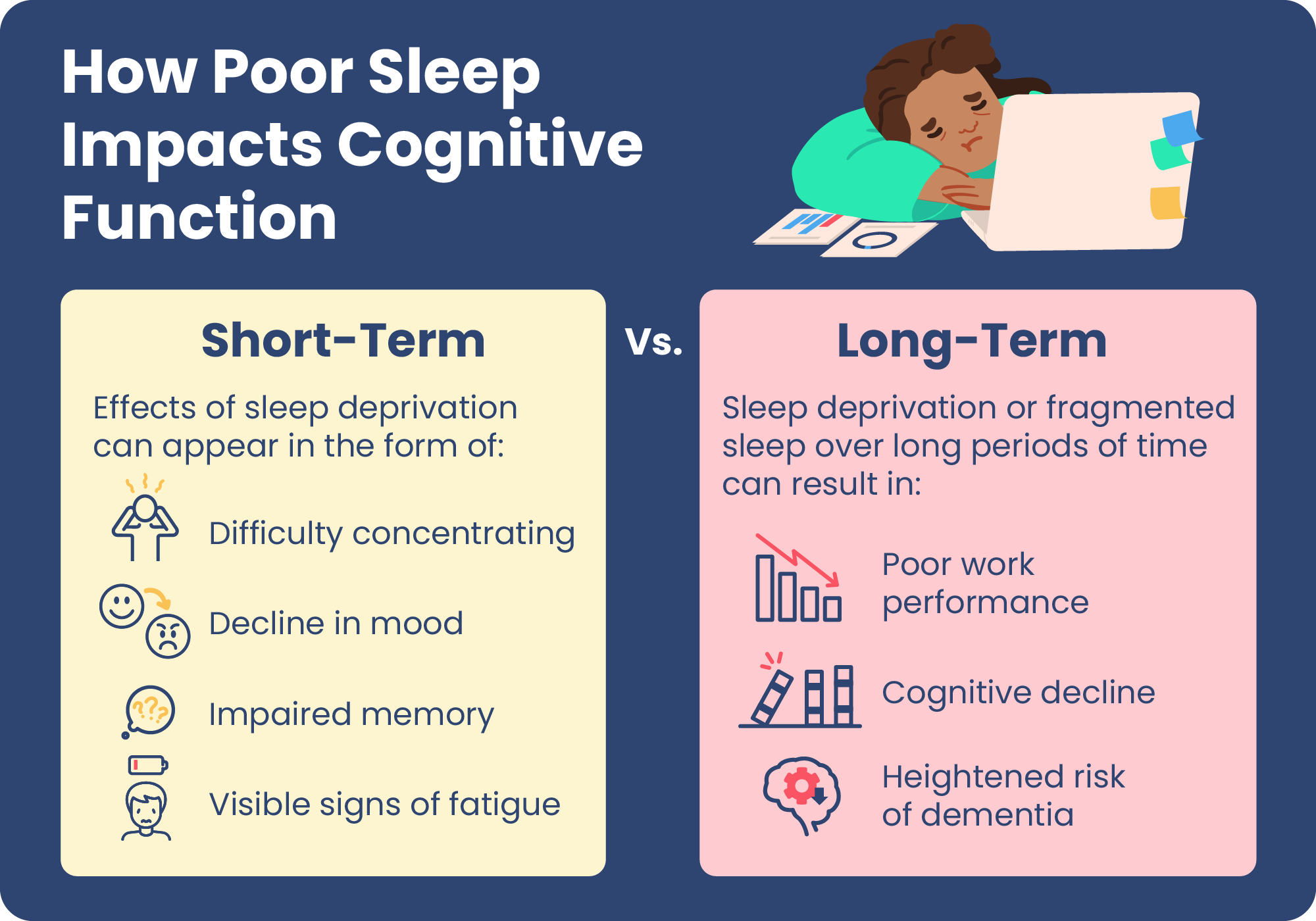
Effects of Sleep Deprivation

The ramifications of inadequate sleep extend beyond immediate fatigue. Chronic sleep deprivation can result in diminished cognitive abilities, including slower reaction times and impaired judgment. Data suggests that individuals operating on limited sleep can exhibit behaviors similar to those of individuals under the influence of alcohol, revealing a significant risk factor for workplace errors and accidents[2][4]. Studies have shown that nearly one-third of American adults get less than the recommended seven hours of sleep per night, a trend that exacerbates issues related to sleep deprivation and productivity[1][3].
The Economic Impact of Poor Sleep

The economic implications of sleep deprivation are profound. Fatigue-related productivity losses cost U.S. companies approximately $136.4 billion annually, translating to around $1,967 per employee. This includes reductions in motivation and productivity, as well as increased health care costs associated with the impacts of poor sleep hygiene[1][3]. Employers facing the repercussions of employee fatigue are encouraged to recognize that sufficient sleep is not merely a personal issue, but a significant factor in overall organizational performance.
Benefits of Quality Sleep

Conversely, improving sleep quality has been linked to enhanced cognitive performance and emotional well-being. A recent study highlighted that increasing sleep duration by just 46 minutes per night can lead to marked improvements in mood and cognitive resilience. Participants who increased their sleep also reported higher levels of gratitude and flourishing—traits that are fundamental to overall well-being and positive work environments[5]. Additionally, even short naps during the day can have significant positive effects on work performance by boosting alertness and reducing fatigue, demonstrating the importance of prioritizing rest in daily schedules[4].
Psychological and Emotional Advantages
Healthy sleep patterns not only enhance cognitive abilities but also significantly improve emotional regulation. Sleep deprivation has been shown to amplify stress responses, leading to increased irritability and vulnerability to emotional disturbances, which can affect workplace relationships and productivity[1][2]. By ensuring adequate sleep, employees may be more equipped to handle work-related stress, fostering better work environments and reducing conflicts.
Practical Steps to Improve Sleep Quality
To mitigate the adverse effects of sleep deprivation on productivity, individuals can implement several lifestyle adjustments:
Assess Priorities: Evaluate activities that lead to staying up late and consider the trade-offs between work, leisure, and proper rest.
Seek Professional Support: Discuss sleep-related challenges with supervisors or human resources, emphasizing the business case for supporting sleep health in corporate culture[1].
Improve Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating an optimal sleeping environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime can foster better sleep quality[2][5].
Consult Healthcare Providers: If sleep issues persist, seeking guidance from medical professionals can lead to tailored solutions for improving sleep[1][4].
Conclusion
In summary, sleep is an essential component of achieving peak productivity. The negative impacts of insufficient sleep on cognitive function, emotional health, and economic performance underline the necessity of prioritizing sleep within both organizational and personal health initiatives. By promoting better sleep habits and recognizing the profound effects of sleep on productivity, individuals and companies alike can foster healthier, more efficient workplaces and enhance overall well-being. Thus, investing in quality sleep is an investment in productivity, effectiveness, and long-term success.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).