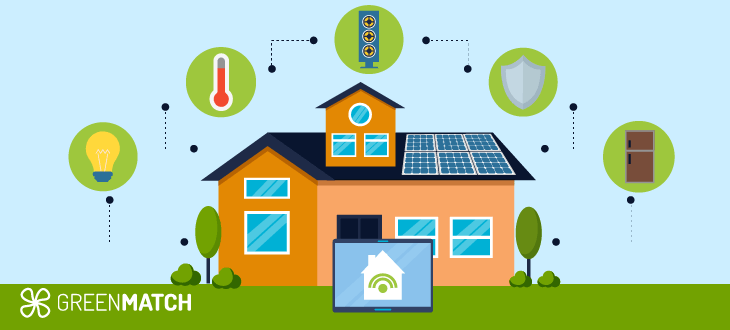
The adoption of smart home devices is reshaping how households manage energy consumption, leading to significant savings and enhanced efficiency. These devices utilize advanced technology to optimize energy use, which can help reduce electricity bills and minimize environmental impact.
Smart Devices and Energy Efficiency

Smart home technologies, such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, and energy-efficient appliances, are designed to improve energy consumption by making homes more responsive to the needs of residents. For instance, smart thermostats can learn from user behavior, automatically adjusting heating and cooling settings according to occupancy patterns and preferences. This feature allows homeowners to save energy without sacrificing comfort, as the system can prevent heating or cooling an empty house. According to reports, the installation of smart thermostats can lead to savings of up to £311 off energy bills annually[7].
In addition to thermostats, smart lighting offers another layer of control and efficiency. These systems can adjust automatically based on the time of day or occupancy—turning off lights in unoccupied rooms or dimming them according to natural light levels. This adaptability not only contributes to lower energy usage but also enhances the overall convenience of home environments[7][8].
Peak Demand Management

Smart home technology also plays a pivotal role in managing energy consumption during peak demand hours. Devices like SmartCharge, developed in research initiatives, intelligently switch between battery power and grid electricity based on real-time energy costs. By managing when energy is drawn from the grid, these systems help reduce strain on electric grids during rush hours, which typically necessitate more expensive energy production methods. In turn, this could lead to reduced costs for both consumers and utility providers[2].
The integration of smart meters facilitates this process further by providing real-time data on energy usage, allowing users to monitor and adjust their consumption patterns to take advantage of lower rates during off-peak periods[8]. This information is instrumental for consumers looking to optimize their energy expenditure, as it encourages shifts in usage to times when electricity is cheaper.
Cutting-Edge Technologies for Savings
The advancements in smart home technologies contribute not only to energy savings but also to a reduction in carbon footprints. Devices such as smart appliances, which are increasingly available in the market, boast energy efficiency ratings that significantly outpace traditional models. For example, energy-efficient refrigerators and washing machines designed with smart capabilities can adapt their operations based on user patterns and external conditions, optimizing energy use throughout their cycles[5][8].
Furthermore, smart home systems can integrate with renewable energy sources, leveraging solar panels and home batteries to maximize the use of green energy. This capability is crucial in enhancing the overall sustainability of a household, allowing for a more significant reduction in reliance on fossil fuels[3][8].
Future Trends in Smart Home Energy Management
As the market for smart home devices continues to grow, more residents are expected to embrace energy-saving technologies. By the end of 2024, projections indicate substantial increases in smart home adoption, with over 20% of UK households utilizing such technologies to optimize their energy usage[3][8]. This trend is set to rise even further, with forecasts suggesting that by 2027, nearly half of all homes will integrate smart technology for energy management[3][7].
The implementation of standardized protocols, such as Matter, aims to facilitate the compatibility of various smart devices across different ecosystems, making it easier for consumers to build comprehensive smart home solutions that enhance energy efficiency. As interoperability improves, users will benefit from seamless automation and better energy management across all their devices, creating a more integrated and efficient home environment[4][6].
The Role of AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another critical factor driving the evolution of smart home technology. AI-enabled devices can learn from household dynamics, adjusting settings proactively to ensure energy savings. For instance, a smart thermostat equipped with AI can make real-time adjustments based on weather patterns and user habits without requiring constant inputs from homeowners. This level of automation not only simplifies usage but ensures maximum efficiency and potential savings on energy bills[4][7][8].
Conclusion
In summary, smart home devices are revolutionizing energy management within households. By offering advanced functionalities that promote efficiency, automation, and integration with renewable energy sources, these devices not only help reduce costs but also promote sustainable living practices. As technology continues to advance and consumer adoption increases, the future of smart homes promises even greater possibilities for energy savings and environmental benefits. The integration of smart technologies is more than just a convenience; it is a vital step toward achieving a more sustainable and efficient way of living.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).