
The transportation sector is poised for a dramatic transformation over the next ten years, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and an urgent need for sustainability. This report outlines how various dimensions of transportation technology are expected to evolve, examining the growth of autonomous vehicles, electrification, data usage, and the development of new mobility services.
Autonomous Vehicles and Innovations
A prominent trend in the upcoming decade is the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles (AVs). Both startups and established manufacturers are focusing on developing semi and fully autonomous cars equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), light detection and ranging (LIDAR), and computer vision technologies. These innovations will enable autonomous last-mile deliveries through drones and driverless trucks, significantly reducing labor costs and improving delivery efficiency[2][8]. The push for autonomous operations will also include the integration of AVs with smart city infrastructure, revolutionizing urban mobility and transporting people and goods more efficiently[8].
Electrification and Energy Solutions
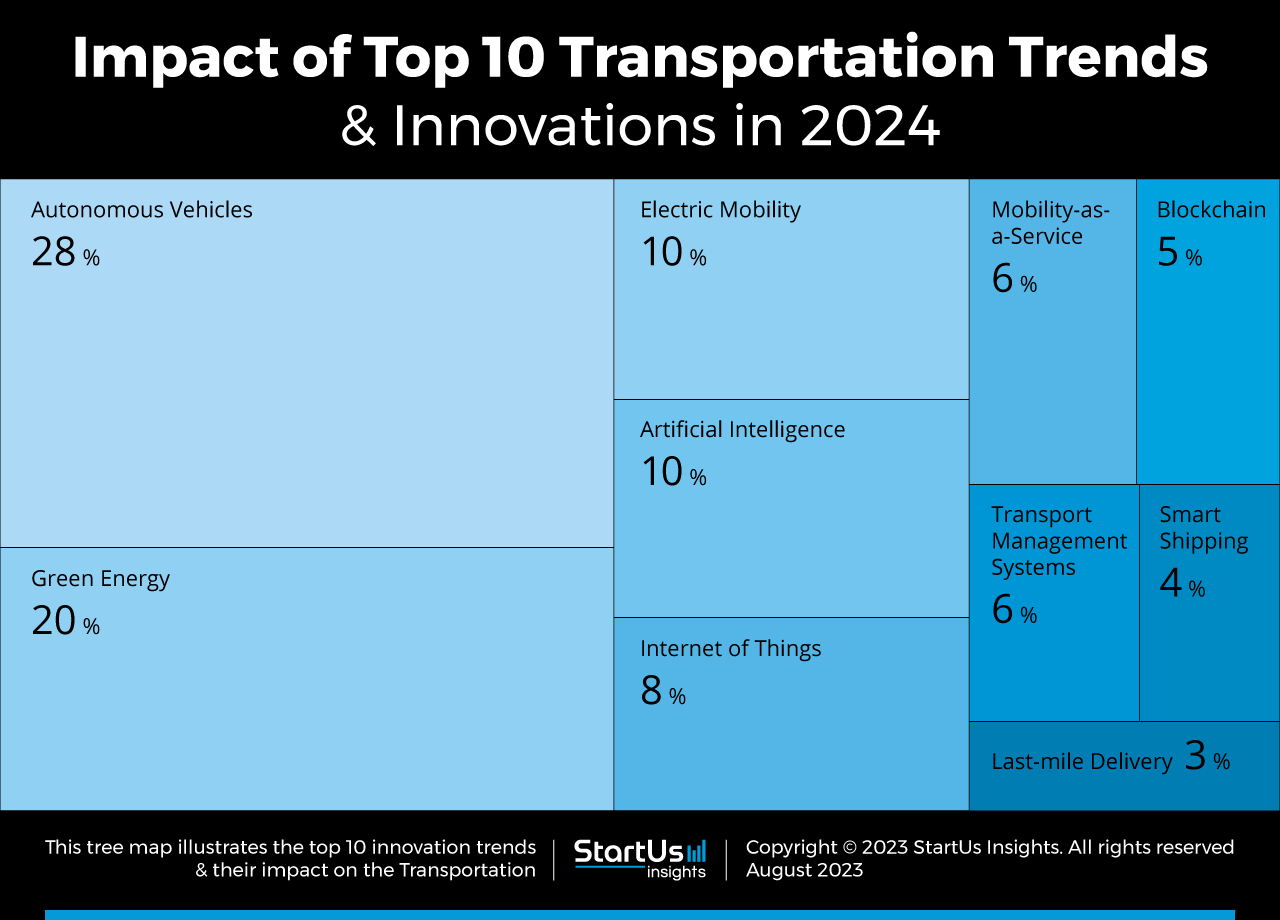
Electrification is another vital area expected to expand dramatically. The availability of advanced electric vehicle (EV) battery technology plays a crucial role in this shift. Innovations like better battery efficiency and new charging infrastructures will alleviate the pressure on public charging networks, making EVs more accessible and cheaper than traditional combustion engine vehicles[5][7]. In addition, emerging technologies like wireless charging will enable effortless energy replenishment for public transport routes, significantly reducing reliance on existing heavy charging infrastructure[5][8].
Furthermore, the introduction of eco-friendly ships and aircraft powered by renewable energy will also gain momentum, marking a significant reduction in carbon emissions associated with transportation[2][7].
Mobility as a Service (MaaS)
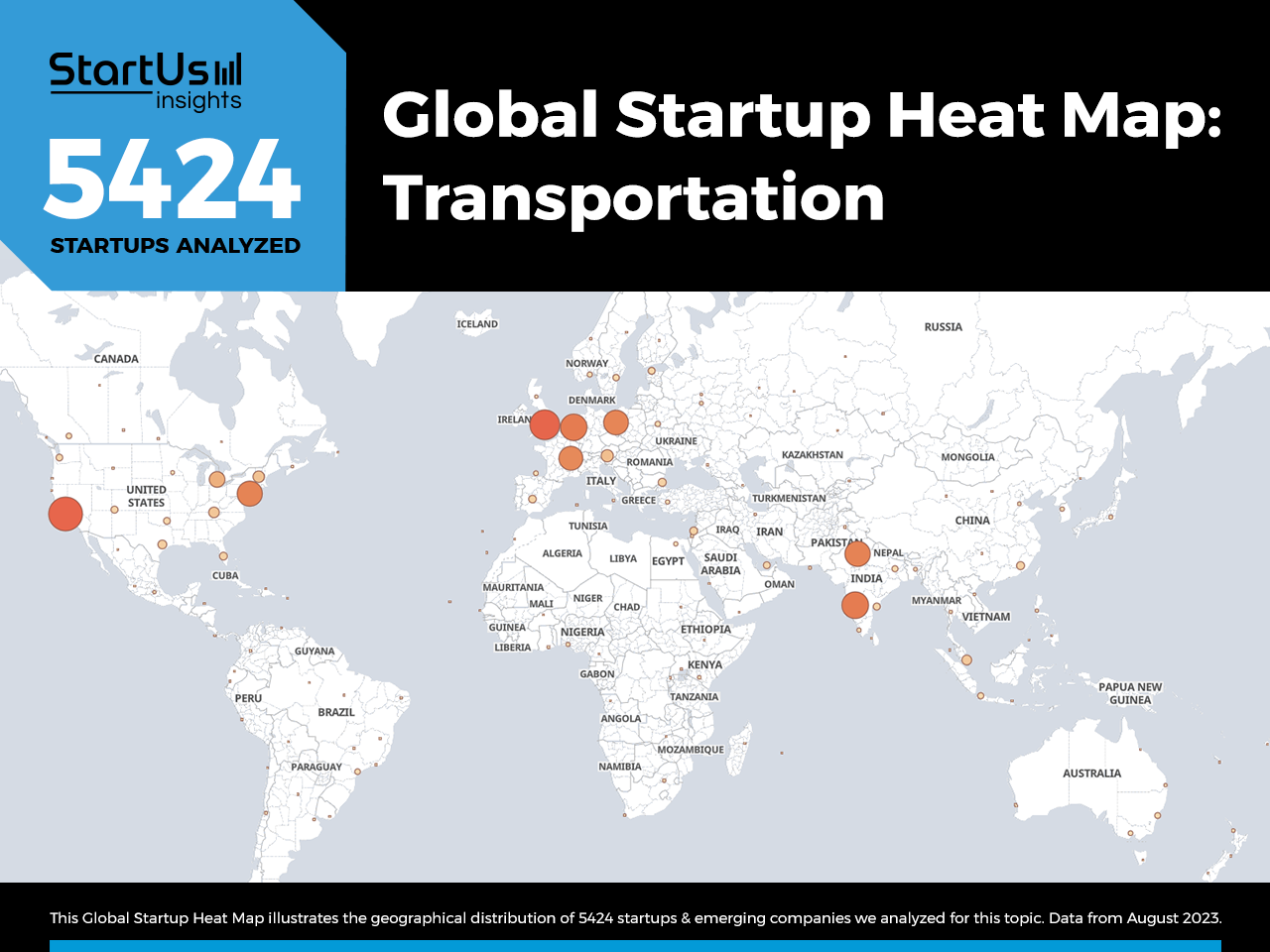
Mobility as a Service is poised to reshape transportation by integrating various forms of transport services into a single accessible offering. MaaS applications allow users to plan journeys using multiple modalities of transport seamlessly and facilitate payments through a single platform. The revenues from MaaS are projected to reach $1 trillion by 2030, reflecting the vast potential of this service model to enhance urban transportation efficiency while reducing congestion and emissions[7][9]. Such systems are essential as urbanization continues to grow; with 68% of the global population projected to live in urban areas by 2050, efficient transport systems are critical[7].
Data and Connectivity
The rising significance of data analytics and connectivity cannot be ignored. Transportation systems will increasingly rely on AI and big data to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making. This integration allows for real-time tracking of vehicles, optimization of traffic flow, and improved safety measures through predictive analytics[3][6]. As vehicles become more connected, data-driven insights will enable advanced traffic management systems, considerably reducing congestion and emissions while enhancing the user experience[6][8].
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Decarbonization remains a top priority for the transportation sector, forming a core aspect of its future development. Government initiatives and public sentiment are shifting toward greener transportation options, with over 150 cities implementing measures to limit private vehicle use and encourage sustainable mobility[1][3]. The transportation sector is currently a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, making sustainability efforts crucial for long-term impact[5][6].
Efforts to adapt to green technologies will be evident within the shipping and freight sectors as well. For instance, the development of hydrogen fuel cell technology and electric aircraft is expected to become more common, supporting transitions away from fossil fuels[4][7][8].
Changing Consumer Preferences

Consumer attitudes towards transportation are changing rapidly as perceived ownership models shift. A notable proportion of potential users are open to replacing private vehicles with shared mobility options. Findings indicate that 46% of respondents in a consumer survey expressed willingness to switch from private cars to alternative transport methods in the coming decade[1]. This shift towards shared and micromobility options further emphasizes the evolving landscape of transportation, where convenience and environmental impact take precedence[8][9].
The cultural shift away from vehicle ownership may also manifest in the rise of subscription-based transportation models, echoing trends seen in other industries like media[4][5].
Conclusion
The next decade will be marked by significant advancements in transportation technology, facilitated by autonomous operations, electrification, and an increasing focus on sustainability. The integration of diverse mobility services and the use of data-driven insights will enhance the efficiency, safety, and enjoyment of urban mobility. As societal norms shift towards greener, more connected options, the transportation landscape will evolve into a more intelligent, seamless, and environmentally friendly ecosystem. The industry is not just adapting to consumer demands but also responding proactively to the pressing need for sustainable solutions in the face of climate change challenges.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).