Overview of Extended Reality in Mental Health Care
Extended Reality (XR) technologies, encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR), are increasingly used in digital therapeutics for mental health. XR provides immersive, computer‐generated environments that allow tailored exposures and engagement in controlled settings. This modality is being explored to address various mental health disorders by enhancing treatment accessibility, reducing stigma, and potentially increasing patient adherence through interactive and engaging interfaces[3][2].
Clinical Evidence for Exposure-Based Treatments in XR
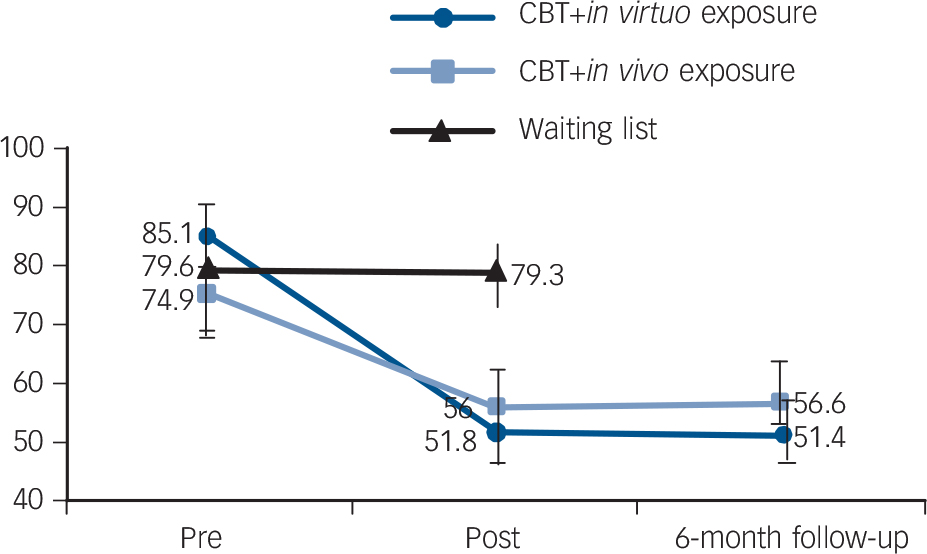
A robust body of clinical evidence supports the efficacy of XR-based exposure therapies, particularly for social anxiety disorder (SAD). Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET) has been shown to create realistic and controllable social environments that enable systematic exposure to feared stimuli. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have reported medium to large effect sizes for VRET when compared to waitlist controls, and its effects are maintained at follow-up periods up to one year[1][5].
Studies have demonstrated that digitally simulated interactions can reduce social anxiety symptoms in both individual and group therapy formats. In particular, controlled trials contrast the efficacy of VRET with traditional in vivo exposure and cognitive behavioral therapy, showing comparable outcomes between these methods[9].
Mindfulness Strategies and Mechanisms in XR Therapies
Beyond pure exposure, XR platforms are being integrated with mindfulness-based strategies to improve treatment outcomes. Mindfulness practices are incorporated to help patients develop nonjudgmental awareness of their internal experiences during exposure sessions, which may facilitate extinction learning and reduce distress over time. Evidence suggests that combining mindfulness with exposure interventions enhances the extinction of distress responses, ultimately reducing reliance on avoidant coping mechanisms[4][10].
Additionally, XR-mediated mindfulness techniques have been employed in treatments such as written exposure therapy combined with app-delivered mindfulness for conditions like PTSD, demonstrating potential benefits in reducing symptoms and comorbidities such as insomnia[6].
Clinical findings point out that while immediate mindfulness-based exposure might initially raise distress levels, continued practice may lead to improved emotional regulation and long-term symptom reduction, underpinning the value of integrating mindfulness into XR exposure protocols.
XR in Group Therapy and Social Anxiety
Another promising application of XR is in the realm of group therapy for anxiety disorders. XR platforms allow patients to interact in virtual spaces using customized avatars, which can enhance nonverbal communication cues and foster a sense of group identification. Digital group therapy in XR can compensate for some limitations observed in traditional video-conferencing, where factors such as reduced eye contact and limited movement often hinder group cohesion. Research indicates that enhanced social identification in XR environments can promote shared support, improve therapeutic alliances, and potentially lead to better treatment outcomes in social anxiety and related conditions[7].
In group settings, the ability to simulate real-world social interactions through controlled VR exposures, combined with group dynamics, may also aid in reducing isolation and enhancing overall engagement in therapy.
Regulatory Pathways and Deployment Challenges
While the clinical promise of XR in digital therapeutics has spurred interest from both clinicians and researchers, several regulatory and practical challenges remain. From a regulatory perspective, establishing approval pathways for XR-based digital therapeutics involves demonstrating measurable efficacy, ensuring user safety, and aligning with established clinical guidelines. For instance, regulatory bodies such as NICE have recently begun to recommend new digital therapies for mental health conditions like depression and anxiety, but fully approved XR interventions remain limited due to the novelty of the technology, the high costs of clinical trials, and the lengthy regulatory review processes[3].
Practical deployment challenges include issues with device accessibility, user familiarity, and integration into existing healthcare systems. Although XR headsets have become more affordable and user-friendly in recent years—with options available across a range of price points—clinicians and patients still face barriers such as limited digital literacy, inconsistent internet infrastructure, and the need for specialized training to effectively use XR tools in therapy sessions. Moreover, early-generation devices suffered from issues related to setup complexity and motion sickness; even though modern devices have addressed many of these shortcomings, overcoming residual skepticism among clinicians remains essential for widespread adoption[3].
Conclusions and Future Directions

Overall, XR technologies are emerging as a versatile and powerful tool in the digital therapeutics landscape, particularly for mental health care. Evidence supports the use of VR-based exposure therapies in reducing social anxiety symptoms as effectively as traditional methods, while the incorporation of mindfulness strategies shows promise in enhancing emotional processing and extinction learning. XR is also being successfully applied in group therapy settings to bolster social identification and engagement, which is especially relevant for treating social anxiety disorders.
Looking ahead, future research should focus on larger-scale and long-term clinical trials that not only refine the integration of mindfulness and exposure techniques into XR platforms but also address regulatory and deployment barriers. Closer attention to the development of standardized usability frameworks, enhanced training for practitioners, and clear regulatory guidelines will be crucial for the integration of XR digital therapeutics into mainstream mental health care. Continued collaboration among clinicians, technologists, and regulatory bodies is likely to facilitate both the development of innovative XR treatments and their practical deployment in clinical settings[1][9].
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).