
Understanding Life Satisfaction
Life satisfaction refers to an individual's cognitive and affective evaluations of their life overall. It is a broader, more stable measure than momentary happiness, encompassing a person’s general feelings of contentment and fulfillment with various aspects of life such as relationships, health, income, and achieving personal goals. According to the literature, life satisfaction is a key indicator of overall well-being and has significant implications for mental health. Research indicates that individuals who report higher levels of life satisfaction also experience better mental health outcomes, including lower levels of anxiety and depression, and higher vitality and self-perceived health[1][7].
In a comprehensive study of life satisfaction, it was found that individuals with poor self-reported mental health experienced particularly low levels of life satisfaction. Those in better self-reported mental health categories showed significantly higher odds of having greater life satisfaction. Specifically, the odds of higher life satisfaction were found to be more than two times greater for individuals reporting fair mental health compared to those reporting poor mental health[1]. This suggests that enhancing mental health can be a viable pathway to improving overall life satisfaction, thus promoting well-being.
Mental Health Outcomes Associated with Life Satisfaction

There is strong evidence linking high life satisfaction with various positive mental health outcomes. Individuals expressing high levels of life satisfaction often demonstrate resilience against mental illnesses and show better coping mechanisms under stress. These individuals are less likely to suffer from psychological distress or exhibit depressive symptoms[2][4]. The presence of supportive social networks plays a critical role in this dynamic; higher levels of social support are associated with increased life satisfaction and, consequently, improved mental health[4].
Conversely, low life satisfaction is associated with adverse health outcomes. A systematic review highlighted that social isolation—an experience resulting in reduced life satisfaction—can lead to detrimental impacts on physical and mental health, such as increased depression, anxiety, and even mortality risks comparable to well-documented risk factors like smoking[8]. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated feelings of social isolation and loneliness, significantly impacting overall life satisfaction and well-being[8].
The Impact of Psychological Well-being
Psychological well-being encompasses various dimensions, including positive affect, functioning, and mental health. Studies have indicated that factors thought to contribute to well-being—such as life satisfaction, self-perceived health, and positive relationships—are positively correlated. For example, a meta-analysis demonstrated that high levels of psychological well-being were linked with protective effects against chronic illnesses like cardiovascular disease and diabetes[2][7]. These findings reinforce the perspective that well-being, measured through life satisfaction, has crucial implications for mental health and physical health outcomes.
Moreover, the relationship between health behaviors and mental health suggests a reciprocal influence. Individuals with healthier lifestyles typically report higher life satisfaction and better mental health. A specific study demonstrated that each additional point in a healthy lifestyle score correlated with a significant reduction in the odds of experiencing negative mental health outcomes such as major depression and generalized anxiety disorder[7]. This correlation underscores the necessity of promoting healthy lifestyle choices as a means to enhance life satisfaction and, by extension, mental health.
The Role of Social Isolation
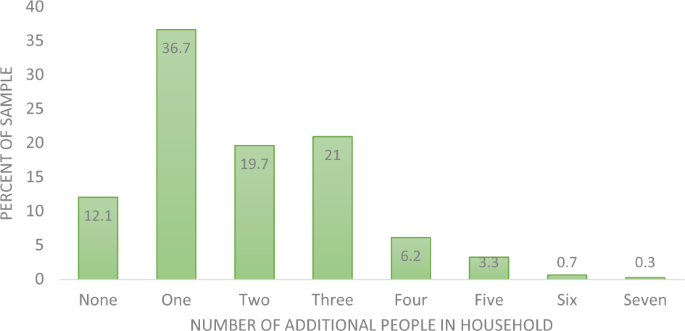
Social determinants, including social support and community connectedness, significantly affect both life satisfaction and mental health. Research emphasizes that social relationships and trust in one's environment are decisive factors contributing to feelings of belonging and overall satisfaction. The experience of social isolation, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, has shown to correlate inversely with life satisfaction, leading to heightened psychological distress among both younger and older adults[8]. Individuals who perceived themselves as socially isolated were also more likely to report lower life satisfaction and mental health issues, highlighting the detrimental effects of perceived isolation regardless of the actual frequency of social interactions[8].
Coping Mechanisms and Strategies
The strategies individuals employ to cope with stress also impact their mental health and life satisfaction. Research has suggested that using positive coping mechanisms, such as seeking social support or engaging in physical activity, can mitigate adverse mental health effects associated with dissatisfaction. In contrast, reliance on negative coping strategies, like substance use, is related to higher perceived social isolation and poorer life satisfaction outcomes[8]. Therefore, developing and encouraging healthy coping strategies could foster improved life satisfaction and mental health resilience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, life satisfaction holds a significant position in the context of mental health, acting as both an indicator and a contributor to psychological well-being. Enhanced life satisfaction is linked with positive mental health outcomes and reduced psychological distress. Conversely, lower life satisfaction correlates with increased risks of mental health issues, often exacerbated by factors such as social isolation. Addressing life satisfaction holistically through improved mental health support, community engagement, and healthier lifestyle choices can promote better health outcomes and enhance overall well-being in diverse populations. As research continues to explore these intricate relationships, it becomes evident that promoting life satisfaction is essential for fostering mental health resilience in individuals across all age groups.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).