
Cooking is an essential aspect of meal preparation that not only enhances flavor but also influences the nutritional quality of food. Different cooking methods affect the retention of vitamins and minerals, with notable differences depending on how food is prepared. Understanding these effects is crucial for optimizing nutrient intake.
Nutritional Changes During Cooking
Cooking methods such as boiling, steaming, frying, and microwaving can significantly alter the nutritional content of foods, especially vegetables. Water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C and the B vitamins, are particularly vulnerable to loss during cooking. For instance, boiling vegetables can lead to substantial leaching of these nutrients into the cooking water. Studies have found that boiling results in the greatest loss of vitamin C, with losses as high as 50% or more in vegetables like broccoli and spinach when subjected to high heat and water immersion[1][2][4].
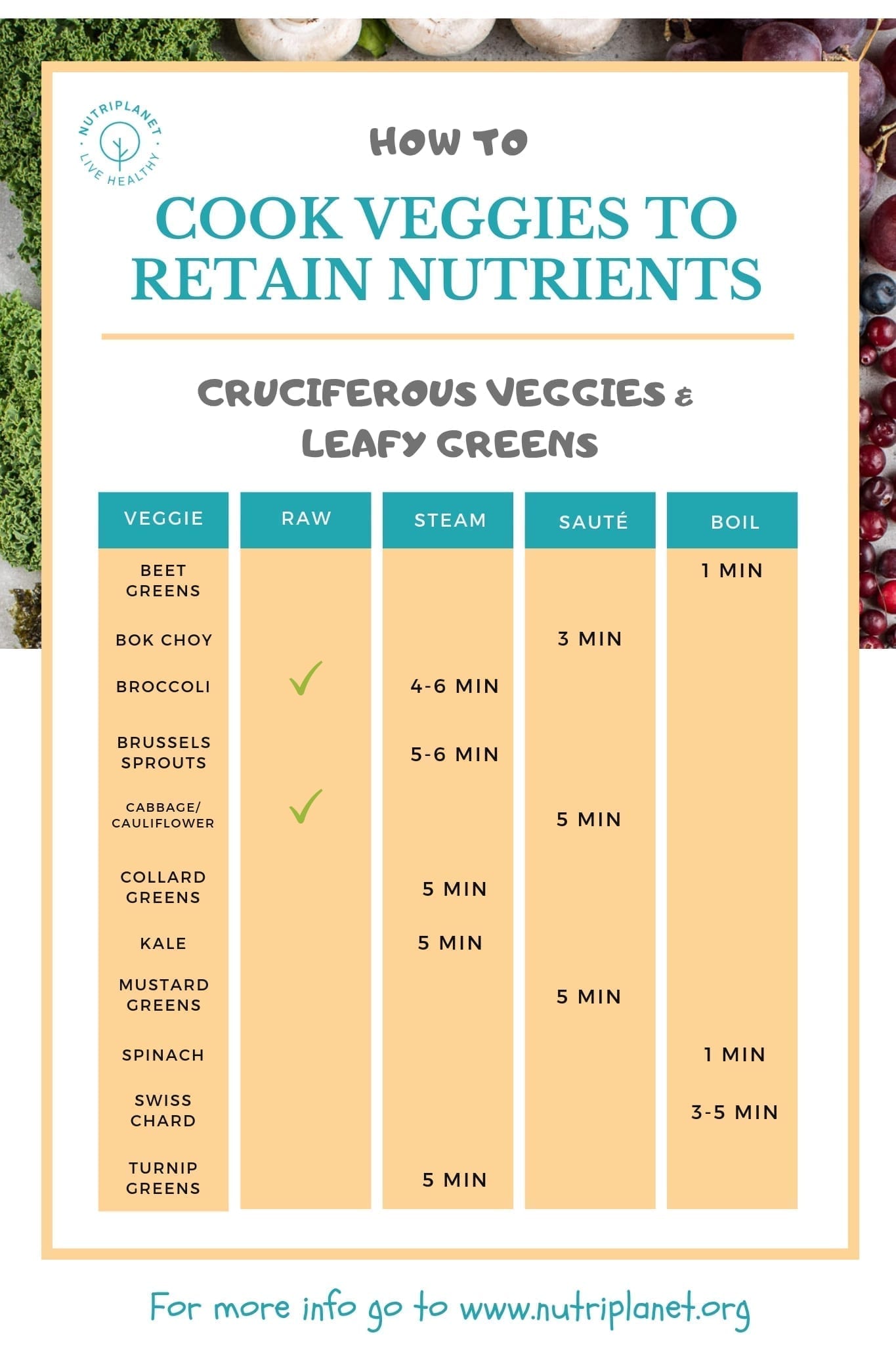
In contrast, steaming is recognized as a more nutrient-preserving method, as it retains more vitamins and minerals by using minimal contact with water and lower temperatures. Research indicates that steaming can preserve a significant amount of vitamin C when compared to boiling, with retention rates generally higher than 90% in certain vegetables[2][3].
Effects of Specific Cooking Methods
Microwaving

Microwaving stands out as one of the best methods for retaining nutrients due to its short cooking times and reduced exposure to heat. Studies suggest that microwaving retains the antioxidant activity of certain foods, such as garlic and mushrooms, more effectively than other methods[1][2]. It has been reported that microwaving can lead to less than 30% loss of vitamin C in green vegetables, which is considerably less than what is observed with boiling[3].
Frying and Grilling
Frying, on the other hand, can present a mixed picture. Cooking foods in oil can enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) while also introducing health risks associated with high temperatures. It is important to note that frying can degrade delicate omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish by as much as 70–85%, while cooking methods like baking cause only minimal losses[1][2][3]. Additionally, grilling and broiling can produce harmful compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are associated with cancer risk. Yet, grilling can enhance flavor and protein retention, although it may also result in the loss of up to 40% of certain B vitamins and minerals[1][2].
Comparison of Methods

When comparing various cooking techniques, studies indicate that the method chosen can make a substantial difference in nutrient preservation. For example, roasted vegetables typically see fewer vitamin losses than those boiled, with minimal impacts on vitamins like C due to the drier heat[1][2]. Sautéing and stir-frying are also healthy methods that can help improve the absorption of certain plant compounds while potentially reducing vitamin C content, particularly in vegetables like broccoli[1][5].
Moreover, the nutritional benefits of specific cooking techniques vary greatly based on the raw food being prepared. For example, while boiling may lead to significant nutrient loss in leafy greens, it may preserve other nutrients well in starchy vegetables like potatoes[2][4].
Impact on Antioxidants
The retention of antioxidants during cooking is a critical area of interest. Antioxidants provide health benefits that can be compromised by improper cooking methods. Microwaving and steaming, as previously mentioned, generally preserve antioxidant levels better than boiling or frying. The scientific literature supports the notion that cooking methods significantly impact the flavonoid and carotenoid content of vegetables, with microwaving often showing higher retention of these beneficial compounds[3][4][5].
Conclusion
Cooking methods undeniably affect the nutritional value of food, influencing vitamin retention, antioxidant levels, and overall health benefits. To maximize nutrient intake, methods such as steaming and microwaving are highly recommended, especially for vegetables. In contrast, boiling, grilling, and frying, while providing unique flavors and textures, pose risks of nutrient loss, particularly for water-soluble vitamins and delicate fats. Therefore, those looking to enhance their dietary quality should consider these factors when preparing meals to ensure they are reaping the full benefits of their food.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).