Introduction

Extended lifespans and increasing life expectancy, a triumph of modern development, have led to profound changes across the financial, healthcare, and technological sectors. Governments, insurers, and fintech companies are all adapting to new demographic realities by rethinking retirement planning, long-term care insurance products, and policy reforms. Research presented in academic venues emphasizes that longer lives bring a host of challenges—for instance, the need to realign pension systems and social support programs with extended retirement periods, while maintaining fiscal sustainability[1].
Policy Reforms and Government Initiatives
Policy makers are actively addressing the financial and social challenges of an aging population. Research from the National Academies highlights numerous proposals aimed at improving the solvency and progressivity of Social Security by considering changes such as raising the early entitlement age (EEA) and normal retirement age (NRA), along with benefit indexation that reflects rising life expectancy[4]. In parallel, the United Nations has documented that almost every country is experiencing population ageing, and many governments have adopted policy measures that promote private savings and active ageing as part of broader strategies to achieve sustainable development goals[12]. Moreover, innovative government strategies, such as those discussed on LinkedIn, emphasize the need for a cohesive national approach—integrating advanced data systems, precision medicine, and fintech—to position countries as leaders in the longevity industry[7].
Long-Term Care Insurance Products and Reforms
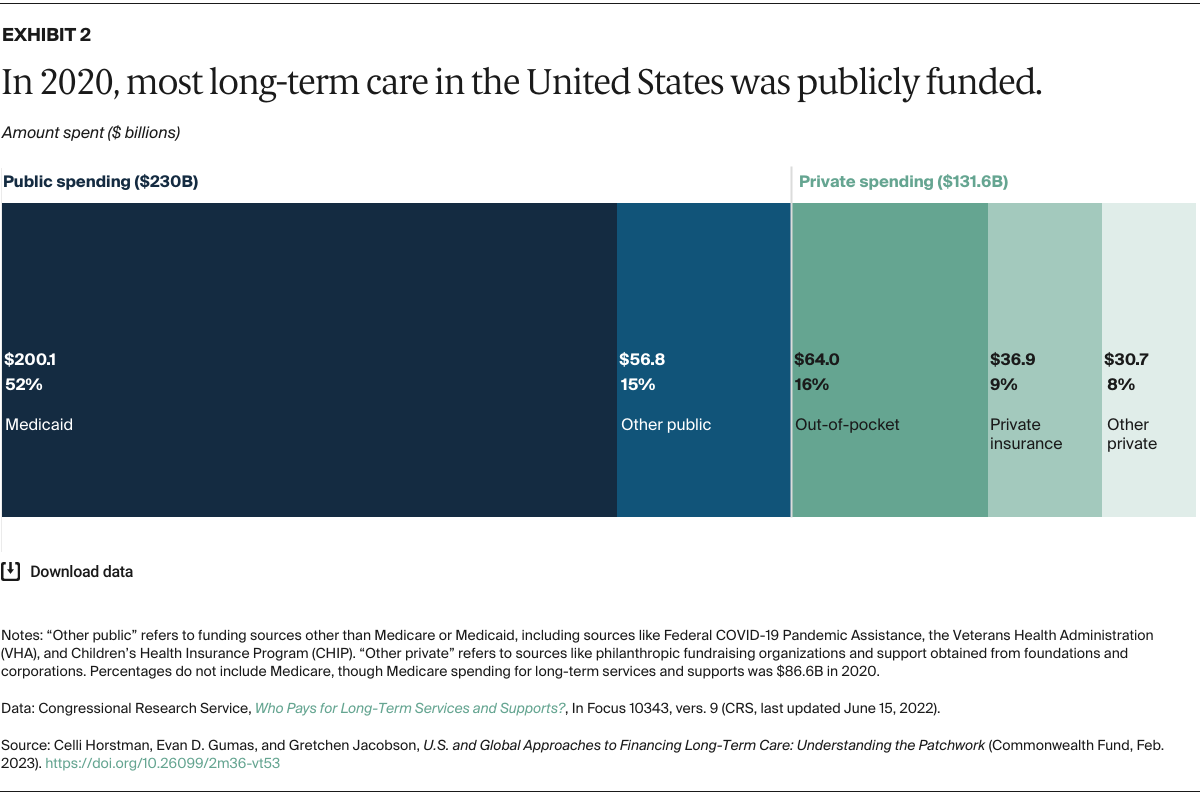
The rise in life expectancy and the corresponding surge in demand for long-term care have placed significant pressure on existing insurance products. According to the Murray Law Office, premium hikes and limited benefit structures are prompting policyholders to review their coverage carefully, with some even considering hybrid policies that combine life insurance with long-term care benefits to achieve greater premium stability and flexibility[5]. Forbes Advisor reviews have identified that current long-term care insurance products are evolving by offering features such as flexible elimination periods and lifetime maximum benefit duration to better align with the extended care needs of an aging population[10]. At the same time, provider-focused insights from Provider Magazine highlight that the long-term care industry is leveraging technology, training, and wellness initiatives to improve operational efficiency and service quality in anticipation of 2025 and beyond[6].
Fintech Innovations in Retirement Planning and Savings
Fintech is fundamentally reshaping the retirement planning landscape by making sophisticated financial tools widely accessible. As Congruent Solutions describes, technology-driven platforms are employing automation, AI-assisted analysis, and mobile applications to demystify investments and boost savings rates among diverse user groups[2]. HiCapitalize further explains that digital platforms streamline the rollover process from 401(k)s to IRAs, significantly reducing administrative burdens and costs, while also democratizing access to professional planning resources[9]. In addition, Forbes has chronicled the emergence of hybrid fintech startups such as Ellevest, Harness Wealth, and Facet Wealth that blend automated investment strategies with personal financial advice, targeting not only high-net-worth clients but also younger investors who are beginning their saving journeys[13].
Integrating Health, Longevity, and Financial Resilience
Beyond pension and retirement savings reforms, there is growing recognition of the need to integrate health initiatives with financial planning. The National Academy of Medicine underscores that while extended life expectancy is a remarkable achievement, it also increases the likelihood of frailty and chronic illness, thereby compounding the need for a robust healthcare and social support system[14]. The World Bank further reinforces that longer, healthier productive lifespans can be achieved by investing in non-communicable disease prevention and human capital development, which in turn supports the broader objective of financial sustainability in old age[15]. Together, these efforts illustrate an integrated approach where advancements in medical care work in tandem with financial and policy innovations to secure a dignified and resilient aging experience.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In summary, the multifaceted approach to financing longevity requires coordinated efforts across public policy, insurance reforms, and fintech innovation. Government-led policy reforms—such as changes to Social Security structures and initiatives to promote lifelong learning and active ageing—are critical in addressing the fiscal challenges posed by an ageing population[4]. At the same time, the insurance industry is evolving its product offerings, with long-term care policies becoming more flexible and responsive to the needs of older individuals, while fintech solutions are revolutionizing retirement planning through enhanced accessibility and lower costs[10][9]. Looking ahead, these converging strategies—supported by advances in digital technology, improved regulatory frameworks, and targeted health interventions—promise to create a more resilient and inclusive system for financing longevity, ensuring that extended lifespans lead to enhanced quality of life and financial security for all.
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).