
Meditation is a widely practiced technique known for its numerous benefits on mental health and emotional well-being. A wealth of scientific research supports its role in reducing stress, anxiety, and depression, enhancing cognitive functions, and promoting a greater sense of overall well-being.
Stress Reduction and Emotional Regulation

One of the most significant psychological effects of meditation is its ability to reduce stress. Research shows that mindfulness practices can drastically lower levels of perceived stress by activating the body's relaxation response, which decreases cortisol production—a hormone associated with stress[4][10]. Regular meditation can help manage stress, allowing individuals to approach challenging situations more calmly. For instance, a systematic review concluded that mindfulness meditation programs significantly improved symptoms of anxiety and depression[6].
Furthermore, meditation has been linked to improved emotional regulation. Individuals who regularly practice mindfulness meditation report increased abilities to manage their emotional responses to stressful situations. This enhanced emotional resilience can lead to a more positive outlook on life and improved interpersonal relationships[2][9]. By fostering a non-judgmental awareness of thoughts and feelings, meditation helps practitioners observe their emotional states without becoming overwhelmed by them, promoting healthier responses to both positive and negative emotions[1][8].
Reducing Anxiety and Symptoms of Depression
Meditation has proven so effective in addressing anxiety that numerous studies advocate its use in therapeutic settings as a complementary treatment for anxiety disorders. In particular, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) has shown to be as effective as traditional antidepressants in preventing relapse in individuals with recurrent depression[9]. The ability of meditation to enhance self-awareness allows individuals to recognize and detach from negative thought patterns—crucial for effective anxiety management[10].
Furthermore, a systematic review analyzing mindfulness meditation’s effects during the COVID-19 pandemic revealed significant reductions in depressive symptoms among participants engaging in meditation practices[3]. Mindfulness training not only alleviates immediate feelings of sadness and anxiety but also contributes to long-term mental health by reducing rumination—excessive focus on distressing thoughts and feelings[1].
Cognitive Enhancements
Beyond emotional benefits, meditation is also associated with various cognitive improvements. Studies have demonstrated that meditation can enhance attention and concentration, making it easier for practitioners to focus on tasks at hand[6]. Techniques such as focused-attention meditation are effective in strengthening cognitive skills, as they train individuals to resist distractions and maintain mental clarity[9].
Additionally, research indicates that mindfulness practices can improve memory. Long-term meditators frequently exhibit increased gray matter density in brain regions associated with learning, memory, and emotional regulation, suggesting that regular practice can contribute to cognitive health and resilience against age-related cognitive decline[5][8] .
Physiological Benefits and their Psychological Impact

The psychological effects of meditation extend to physical health as well. Evidence suggests that meditation can enhance immune function, reduce blood pressure, and decrease inflammation, which indirectly supports mental health by mitigating the physical effects of chronic stress[4]. For example, studies have shown significant impacts on inflammatory markers and greater cardiovascular functioning among regular meditators, which can foster feelings of physical well-being and reduce anxiety about health[9][5].
Such physiological improvements bolster the psychological benefits of meditation, creating a positive feedback loop. Feeling physically better may contribute to enhanced mood and a greater capacity to engage in social and personal activities, thereby enriching overall quality of life[8][9].
Techniques and Accessibility

There are various forms of meditation, each targeting different aspects of mental health. Mindfulness meditation encourages a present-focused awareness, while techniques like loving-kindness meditation foster compassion and empathy[10][5]. Research suggests that even brief, self-administered mindfulness exercises can effectively reduce stress, enhance pleasure, and improve emotional states[7].
The accessibility of meditation through diverse formats—such as online courses and smartphone apps—has further facilitated its adoption. Users can engage in mindfulness at their convenience, ensuring that they can maintain their practice without significant time constraints[9][10].
Conclusion
In summary, meditation offers extensive psychological benefits, including stress reduction, emotional balance, enhanced cognitive functions, and improved physical health. Supported by scientific evidence, mindfulness practices continue to emerge as effective, accessible means of promoting mental well-being in various populations. Regular meditation can help cultivate a more resilient mindset, fostering personal growth and enhancing overall quality of life in an increasingly stressful world.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
The Luminous Beetle: How West Indies Inhabitants Used the Cucujus Fire-fly
Historical accounts from the West Indies reveal the remarkable resourcefulness of its inhabitants in their use of a native luminous beetle known as the Cucujus (Elater noctilucus)[1]. Far more than a simple curiosity of nature, this fire-fly was an integral part of daily life, serving a multitude of functions that ranged from the highly practical to the purely decorative. These insects provided a sustainable and readily available source of light for nighttime activities, guided travelers through the darkness, and were even incorporated into festive attire and rituals. This report explores the diverse and ingenious applications of the Cucujus, drawing from historical narratives that paint a vivid picture of its role in the culture and society of the West Indies.
The Cucujus Fire-fly (Elater noctilucus)
A specimen of the Elater noctilucus, also known as the Headlight Elater or Cucujus. The two large spots on its thorax emit a powerful, steady bioluminescent glow.
A Living Lantern: Practical Uses for Illumination
The most fundamental use of the Cucujus was as a source of light, effectively a living, self-powered lantern. The glow emitted by these beetles was bright enough to enable a variety of tasks that would otherwise be impossible after sunset. Historical records describe how the fire-flies transformed the night, allowing domestic and personal activities to continue in their steady, cool light[1].
Domestic Life by Fire-fly Light
An artistic interpretation of a West Indies household in a historical setting, where inhabitants are sewing and reading by the collective glow of Cucujus fire-flies held within a perforated gourd cage.
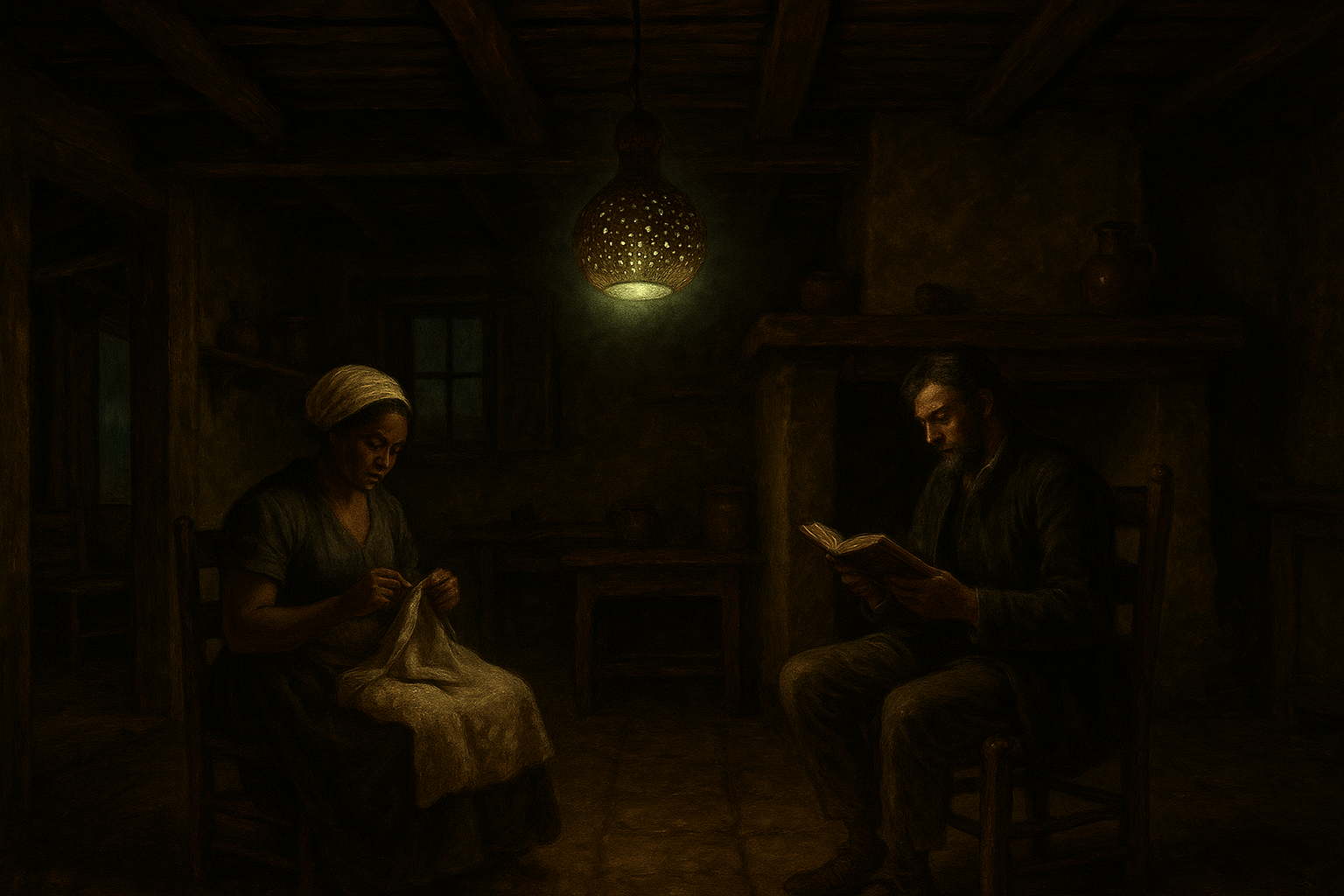

Household and Domestic Lighting
Within the home, the Cucujus served as an all-purpose lamp. According to an old translation of Peter Martyr's History of the West Indies, the light was sufficient for a wide range of detailed work. The text notes, "so that the Inhabitants spinne, sewe, weave, and daunce by the light of the flying Cucuji. Our men also read and write by that light"[1]. This demonstrates that the beetles' luminescence was not merely ambient but strong enough for tasks requiring focus and precision. In more recent times, the naturalist Humboldt observed that among poorer households in Cuba, a simple perforated gourd containing a dozen fire-flies was enough to provide light for an entire night[1]. This practice highlights an economical and accessible lighting solution for the general populace.
The utility of these fire-flies extended beyond the home to situations where conventional lights were impractical or forbidden. One account tells of a lady from Trinidad who, while on a ship where open flames were prohibited for fear of attracting privateers, used Cucujus beetles to provide the light she needed to breastfeed her child during the night[1].
Guidance for Night Travel and Activities
For those venturing out after dark, the Cucujus was an indispensable guide. Travelers devised an ingenious method for hands-free navigation by tying two fire-flies to the great toes of their feet[1]. This illuminated the path directly before them, preventing stumbles and falls in the dark terrain. In addition to lighting their way, they would carry another beetle in their hand to help them hunt for small local animals known as 'Hutiae'[1]. The fire-flies were also employed to facilitate night fishing, their glow likely used to attract fish or simply to see by the water's edge[1].
Beyond Light: Decoration, Ritual, and Pest Control
The applications of the Cucujus fire-fly went far beyond simple illumination. The inhabitants of the West Indies integrated these living lights into their culture, entertainment, and even household maintenance in creative ways.
- Personal Adornment: The beetles were used as living, sparkling jewels. In the Spanish Colonies, young people would tie great numbers of them to their garments and even to their horses during festivals, creating a spectacular moving display of light as they rode through the streets[1]. In later times, this practice evolved into a high-fashion statement, with ladies wearing as many as fifty to one hundred Cucujus on a single ball-room dress as a dazzling ornament[1].
- Ritual and Entertainment: For amusement or to create a frightening spectacle, people would rub their faces with the flesh of a dead Cucujus, causing their skin to "shine like a flame of fire"[1]. A similar practice was observed among the Caribbee Islanders, who would anoint their entire bodies with the juice squeezed from the beetles for certain solemnities where candles were forbidden, making themselves glow in the dark[1].
- Pest Control: The Cucujus also served a practical purpose inside the home as a form of biological pest control. When released indoors, the beetles would hunt and consume gnats, allowing the inhabitants to rest peacefully without being bothered by biting insects[1].
An Unintentional Tool of Warfare
Perhaps the most dramatic role the Cucujus played was in military encounters, where its natural glow led to significant confusion and miscalculation. The swarms of fire-flies were mistaken by newly arrived Europeans for the lit matches of an opposing army's matchlock muskets, creating the illusion of a much larger and more prepared fighting force.
The Fire-fly Deception
An illustrative depiction of European soldiers, like those under Sir Thomas Cavendish, landing on a West Indies shore at night and retreating in alarm, mistaking swarms of Cucujus fire-flies in the trees for the lit fuses of a large enemy force.
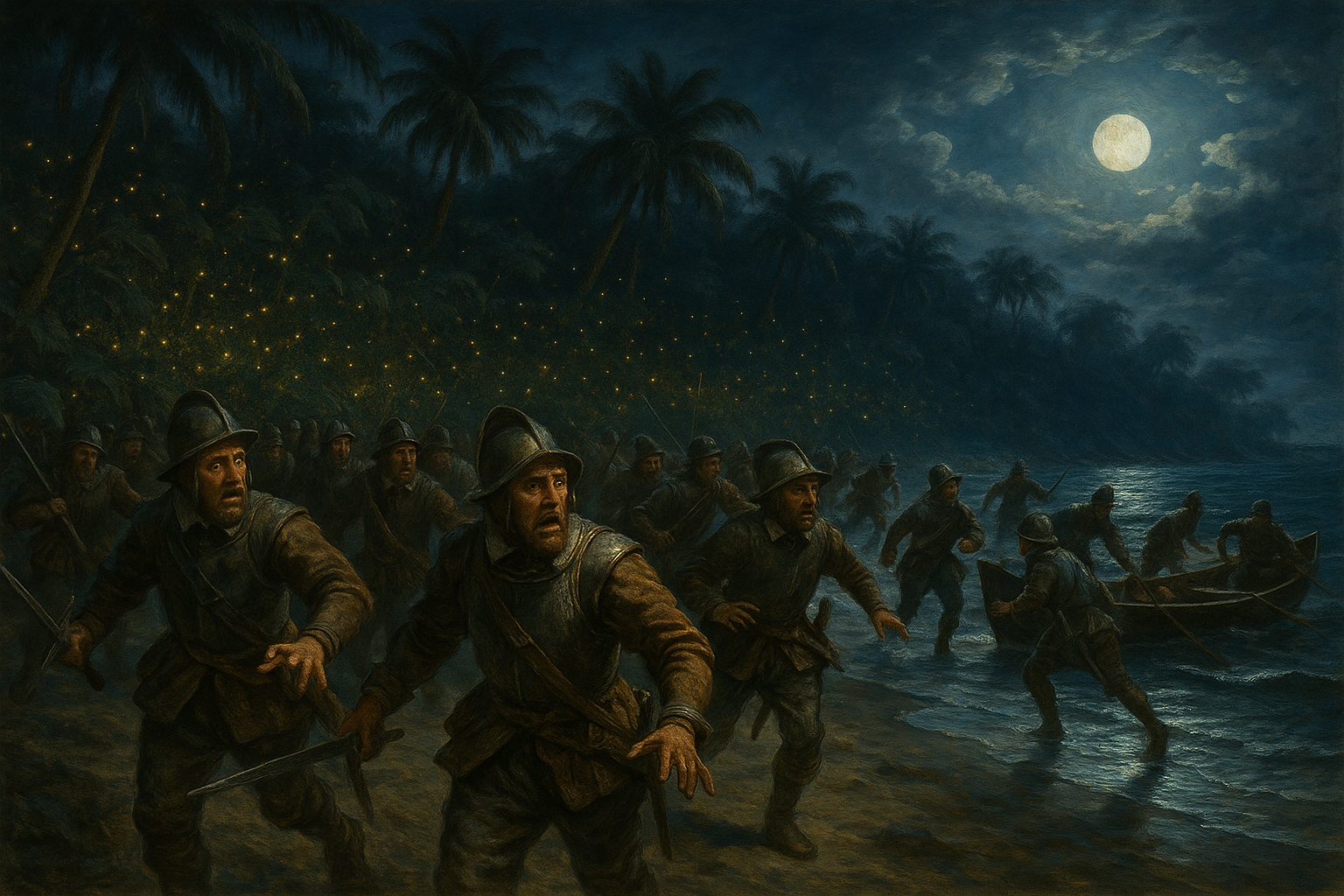

This natural phenomenon had real strategic consequences. Historical accounts note that when English explorers Sir Thomas Cavendish and Sir Robert Dudley first landed in the West Indies, their forces were so intimidated by the sight of these countless lights in the woods that they believed a Spanish army was waiting for them. This misinterpretation caused them to retreat to their ships, effectively repelled not by human soldiers, but by a swarm of insects[1].
Conclusion
The Cucujus fire-fly was far more than a simple insect to the inhabitants of the West Indies; it was a multifaceted natural resource. Historical records illustrate how its bioluminescence was ingeniously applied to solve everyday problems, from providing light for domestic chores and nighttime travel to controlling pests. Beyond its practical utility, the fire-fly was woven into the cultural fabric of the region, used as a stunning form of personal decoration and for ritualistic purposes. The accounts of these beetles unintentionally deceiving military forces further underscore their significant, if sometimes accidental, impact. The story of the Cucujus is a compelling example of human ingenuity and adaptation, showcasing a deep and resourceful relationship with the natural world.
References
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.

They found above that Bread, a shrine Rear'd by the harmless race!
Mr. Hawker[1]
A low sweet psalm, that grieved within In mournful memory of the sin!
Mr. Hawker[1]

...our hummings you speak of are as so many hymns to the Great God of Nature...
Bee (character in Howell's Par…[1]
...the choirs of Bees singing about it, and keeping watch in the night, as monks do...
Butler, quoting Thomas Bozius[1]
...they melodiously sang to Him songs of praise as they were able...
The School of the Eucharist[1]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Mashed lady-birds were put into hollow teeth to relieve toothaches.
Stag-beetles were tied around children's necks to help them retain their urine.
Bed-bugs were given by country people as a cure for fever and ague.
Country people swallowed lice to cure jaundice.
Bot-fly larvae from sheep heads were prescribed as a remedy for epilepsy.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Transcript
Did you know that throughout history, insects have been seen as much more than just tiny creatures? A book from 1865 called 'Curious Facts in the History of Insects' collects all sorts of legends, superstitions, and bizarre uses for bugs, from medicine to art. For instance, some cultures have used insects as living jewelry! In Brazil, ladies would form necklaces out of brilliant golden beetles. And in the Spanish Colonies, young people would decorate their clothes and even their horses with hundreds of glowing fireflies for festivals, creating a moving body of light on dark evenings. But perhaps the strangest story is about a lawsuit that lasted for over forty-two years between the people of a French village and a species of beetle! The villagers even offered the insects their own fertile plot of land to try and settle the case. And get this: in one Swedish town, the way they chose their new mayor was by placing a louse in the middle of a table and seeing whose beard it crawled into first! Makes you wonder what other strange roles insects have played in our history, does it not?
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalised discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
:strip_icc()/BHG-home-improvement-advice-expert-advice-how-to-remove-stripped-screw-hero-4e5488246e9d4240ba33c56d02f6b41d.jpg)
To remove a stripped screw without special tools, try some common household methods. Placing a rubber band over the screw head can help increase friction, allowing your screwdriver to grip better. Simply insert the screwdriver into the rubber band and turn it counterclockwise until the screw loosens[5]. Another technique involves using locking pliers to grip the screw's head directly, turning it to remove it[3].
For prevention, ensure you're using the correct screwdriver bit size to match the screw. Apply even pressure and keep the driver perpendicular to the screw while turning to avoid slipping and stripping in the first place[6].
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).

Information used to be the scarce commodity. Attention is now the scarce commodity.
Laurie Spiegel[2]
The computer is actually a folk instrument.
Laurie Spiegel[2]

Music is a fundamental human experience.
Laurie Spiegel[4]
Composing is improvisation slowed down with a chance to go back and fix the bad bits.
Laurie Spiegel[5]
Artistic creativity is an essential method of processing the intensity of being alive.
Laurie Spiegel[4]
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).
Curious Facts in the History of Insects: A Victorian Exploration of Entomology and Folklore
Published in 1865, Frank Cowan's Curious Facts in the History of Insects presents a comprehensive compilation of legends, superstitions, and historical accounts related to insects, spiders, and scorpions[1]. The work is not a scientific treatise on the natural history of insects; rather, it is a deliberate collection of what the author terms 'extra-scientific facts' gathered from chronicles, histories, and travelogues[1]. Cowan's primary objective was to increase interest in the science of entomology by showcasing the rich tapestry of human belief and culture that has been woven around these creatures throughout history[1].
Cowan, who began the work at the Congressional Library in Washington during the winter of 1863-4, makes a crucial distinction about his methodology[1]. He positions himself as a historical compiler, not a scientific verifier. He clarifies that he does not vouch for the scientific truth of every belief recorded, but for the historical accuracy of its existence in literature and folklore[1]. For Cowan, the fact that Pliny claimed beetles could be used as remedies is historically true, regardless of the remedy's actual efficacy[1]. This approach provides a unique window into the multifaceted and often contradictory relationship between humans and the insect world, a relationship defined by fear, reverence, utility, and artistry.
Insects as Omens and Agents of Divination
A significant portion of Cowan's work is dedicated to the role of insects in superstition and folklore, where they frequently appear as omens or tools for divination. These beliefs span a wide spectrum of human emotion, from joy and hope to terror and dread. The interpretation of an insect's appearance often depended heavily on cultural context and the specific species encountered.
- The Lady-bird: Widely seen as a 'harbinger of joy,' the Lady-bird was associated with good fortune and fine weather[1]. In Scandinavia, it was dedicated to the Virgin Mary[1]. It was also used in love divination, with young girls in Norfolk reciting rhymes to the insect to predict when they would marry[1].
- The Death-watch Beetle: In stark contrast, the clicking sound made by the Death-watch beetle (Anobium tessellatum) was a source of widespread fear, believed to be an 'omen of the death of some one in the house wherein it is heard'[1].
- The 'Coffin-cutter': In Ireland, a large beetle known as the 'Coffin-cutter' was viewed with suspicion, with the populace believing it was connected in some way to 'the grave and purgatory'[1].
- The Siamese Dream-book: Cowan references a Siamese text that provides interpretations for various encounters with insects[1]. For example, an insect falling and striking a person's face was a sign that the individual would soon marry[1].
The Entomological Apothecary: Insects in Historical Medicine
The book details a vast and curious pharmacopoeia derived from the insect world. For centuries, insects and their byproducts were prescribed for a wide range of ailments, reflecting a medical tradition where observation and superstition were often intertwined.
A Victorian Apothecary's Shelf of Insect Remedies
An assortment of glass jars and vials on wooden shelves in a dimly lit Victorian apothecary. The jars contain various insects like beetles, spiders in webs, and dried caterpillars, with handwritten labels indicating their medicinal uses such as 'For Ague' or 'Toothache Remedy'. The atmosphere is scholarly and slightly mysterious.

- Lady-birds were considered an effective remedy for colic and measles, and were frequently recommended as a cure for toothaches[1].
- Stag-beetles had multiple uses; their mandibles were used as an absorbent for pains, and an oil derived from the insects was dropped into ears to treat earaches[1].
- Spiders and their webs were common in folk medicine. Pills made from spider webs were considered an 'infallible cure for the ague'[1], and the webs themselves were used to stop bleeding from cuts, a practice mentioned by Shakespeare[1].
- Chinese Medicine: Cowan records that in China, the tail of a 'very deformed insect' was dried and powdered to be given to women in labor, as it was believed to 'forward their delivery'[1].
A Culinary History: The Practice of Entomophagy
Cowan documents that the practice of eating insects, or entomophagy, was far from a novelty, but a dietary staple in many cultures around the world. Insects provided a vital source of nourishment, and in some cases, were considered great delicacies.
- The Grou-grou: The large, white larva of the Palm-weevil, known as the Grou-grou, was considered 'one of the greatest dainties in the West Indies' when fried or broiled[1].
- Locusts: For Arabs in the Sahara, locusts were a crucial food source. They were prepared by being roasted, dried, and pounded into a sort of pudding or eaten whole after removing the head, wings, and legs[1].
- Silkworm Pupae: In China, the pupae of silkworms were not discarded but were eaten and 'considered delicacies'[1].
- Centipedes: The naturalist Humboldt observed Indian children in South America digging up and eating large centipedes, some of which were eighteen inches long[1].
Art, Adornment, and Imperial Symbols
The natural beauty of insects, with their iridescent colors and intricate forms, has long inspired their use in art and personal adornment. From jewelry and embroidery to religious icons and imperial symbols, insects have been incorporated into human material culture across the globe.
Personal Adornment and Jewelry
- Beetle Jewelry: In Chili and Brazil, women fashioned beautiful necklaces from 'golden Chrysomelidae and brilliant Diamond-beetles'[1]. The iridescent wing-cases (elytra) of certain beetles were used to embroider dresses in China, England, India, and Ceylon[1][1].
- Luminous Ornaments: Fire-flies (Cucujus) were used as living jewels in the West Indies and Spanish Colonies, where they were tied to garments or worn in the hair to create a dazzling, moving display of light[1]. In Italy, gentlemen would adorn the hair of ladies with glow-worms on summer evenings[1].
- Butterfly Head-dresses: The book notes the contemporary fashion of French and American ladies wearing butterflies on their head-dresses[1].
Symbolism in Art and Governance
Beyond mere decoration, certain insects were imbued with profound symbolic meaning, representing deities, creative power, and imperial authority. These symbols were carved into monuments, stamped onto currency, and woven into the very fabric of power.
- The Sacred Scarab: The Scarab beetle (Ateuchus sacer) was a central figure in ancient Egyptian religion and art[1]. As a symbol of the sun and creation, it was worshiped, carved into gems and monuments, and placed in tombs[1]. This artistic form was later adopted by the Etruscans and Greeks for their gems[1].
- The Imperial Bee: Cowan recounts the theory that the golden bees found in the tomb of the Frankish king Childeric were the origin of the Fleur-de-lis in the Arms of France[1]. Centuries later, Napoleon I and II had their imperial robes embroidered with these same golden bees[1].
- Insects on Currency: Bees were depicted on an American Continental forty-five dollar bill from 1779, and the effigies of locusts were perpetuated on ancient coins[1][1].
Plagues, Phenomena, and Passionate Collectors
The book also chronicles remarkable historical events and strange phenomena attributed to insects, as well as anecdotes revealing the profound passion some individuals have held for entomology.
- Devastating Plagues: Cowan recounts numerous historical accounts of locust swarms causing immense destruction, famine, and pestilence[1]. One such plague in Africa was said to have caused a pestilence that killed 800,000 people in the kingdom of Massinissa alone[1].
- 'Showers of Blood': The mysterious phenomenon of 'showers of blood' is explained as the red fluid discharged by vast numbers of butterflies and other insects upon emerging from their pupal state[1].
- Passionate Entomologists: An anecdote describes General Count Dejeau, an aide to Napoleon, who was so devoted to collecting that he pinned insects to his hat even during battle. After being struck in the head at the battle of Wagram, his first words upon recovering were, 'I am not dead but, alas! my insects are all gone!'[1].
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Relationship
Frank Cowan's Curious Facts in the History of Insects provides a rich and detailed summary of the historical relationship between humanity and the insect world. The book demonstrates that insects have been far more than just pests or objects of scientific curiosity. They have been deities, omens, medicines, food sources, artistic muses, and symbols of imperial power[1]. Cowan's work successfully achieves its goal of making entomology more engaging by showing that the story of insects is inextricably linked to the story of human culture, belief, and history.
References
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).


