Introduction to Meditation Styles
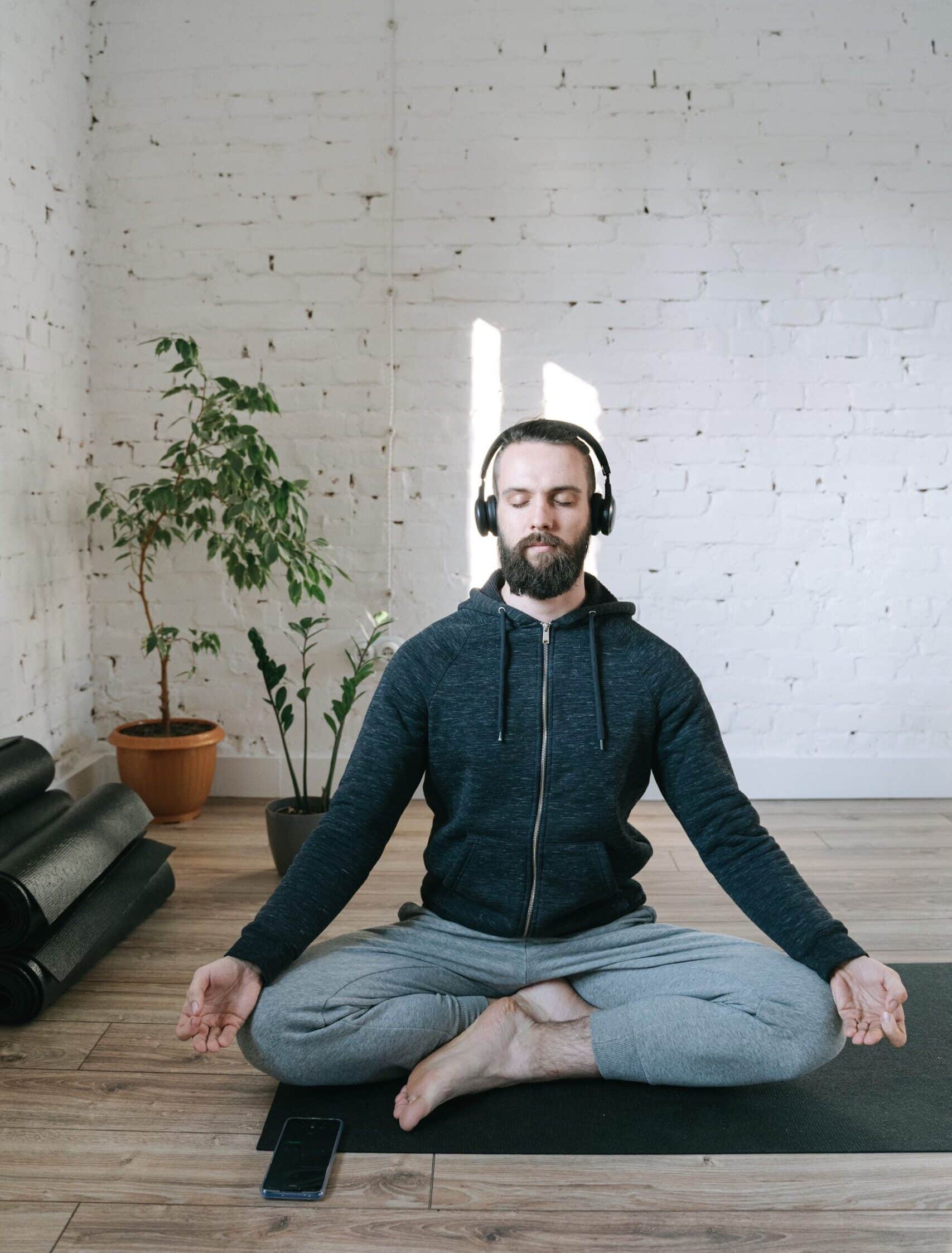
Meditation can be practiced in many ways, and two common methods are guided meditation and unguided (or silent) meditation. Both approaches aim to promote relaxation, stress relief, and enhanced mindfulness; however, they differ in terms of structure and the degree of external input. In guided meditation, practitioners follow directions provided by a teacher or audio recording, while unguided meditation is a self-directed practice where the meditator controls the entire process[1][2][6].
Characteristics of Guided Meditation
Guided meditation relies on an external source – such as an instructor’s voice, a prerecorded audio track, or a meditation app – to direct the practitioner through specific techniques. As noted across multiple sources, guided sessions commonly include clear instructions on breathing, focus points (such as body scans or visualizations), and even cues for emotional processing[1][2][4]. Beginners find this approach especially useful because it helps reduce the tendency for the mind to wander, provides a structure to build a regular practice, and can be tailored to address specific needs like stress relief or improving sleep[1][5][8]. In some cases, guided meditation techniques are designed to gently lead one’s awareness from everyday thoughts to a more peaceful and mindful state, ensuring that the meditator does not get lost in distracting thoughts[4][6].
Characteristics of Unguided Meditation

Unguided meditation, also known as silent or independent meditation, is characterized by the absence of external guidance. In this practice, the meditator sits alone and directs their focus—whether on the breath, body sensations, or a mantra—without following a preset script[2][6]. This method places full responsibility on the practitioner to maintain concentration and navigate their own experience. Advanced meditators often prefer unguided meditation because it allows for a deeper level of introspection and personal expression, offering greater freedom to explore one’s inner thoughts without interruption[4][9][11]. However, for beginners, this lack of structure can sometimes make it challenging to maintain focus, especially if the mind tends to be “chatty” or easily distracted[6][9].
Comparing Benefits and Limitations
Both guided and unguided meditation have unique benefits and drawbacks:
• Guided meditation is praised for its structured format and ease of use, especially for newcomers. The explicit verbal cues help reduce anxiety, heighten concentration, and offer a clear path for beginners to understand meditation techniques. Additionally, many guided sessions are designed with specific intentions—such as stress reduction or emotional healing—in mind, which can be particularly helpful when facing challenging situations[1][4][5][8].
• In contrast, unguided meditation offers a higher level of autonomy and adaptability. Without reliance on external prompts, practitioners develop the ability to maintain focus independently and cultivate a personal, introspective experience that can lead to deeper mindfulness and self-awareness over time. However, this freedom may come at the cost of structure, making it more challenging for beginners who might struggle with sustaining attention without a guiding voice[2][6][9].
Ultimately, the trade-offs between dependence on external guidance and the freedom to create one’s own meditative flow shape the effectiveness of each style, depending on the experience level and personal preferences of the meditator[7][10].
Choosing the Right Practice
Deciding whether guided or unguided meditation is best for an individual depends on several factors. Beginners, or those who have difficulty maintaining concentration, are generally advised to start with guided meditation due to its step-by-step instructions and immediate cues that help anchor the mind[1][3][5]. As one's practice deepens and confidence increases, transitioning to unguided meditation can foster independence, enabling personal exploration and greater internal focus[9][10][11]. Some practitioners even choose to alternate between the two methods, using guided sessions when they need focused relaxation and turning to unguided practice when they desire a more introspective, free-form meditation experience[12][13]. This flexibility allows each individual to tailor their meditation routine to their current mood, goals, and level of experience.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary difference between guided and unguided meditation lies in the source of direction. Guided meditation offers structured verbal guidance—making it ideal for beginners and those seeking targeted benefits—while unguided meditation provides an opportunity for deep personal exploration without external input. Both methods can lead to enhanced relaxation, improved focus, and greater self-awareness, but the choice ultimately depends on one’s experience level, personal needs, and goals. Whether one opts for the clear structure of guided meditation or the liberated form of unguided practice, both paths can be valuable components of a balanced meditation routine[1][2][4][9].
Get more accurate answers with Super Pandi, upload files, personalized discovery feed, save searches and contribute to the PandiPedia.
Let's look at alternatives:
- Modify the query.
- Start a new thread.
- Remove sources (if manually added).